Recognition of Expenses
Expenses are outflows of cash or other valuable assets from a person or company to another entity. This outflow of cash is generally one side of a trade for products or services that have equal or better current or future value to the buyer than to the seller. Technically, an expense is an event in which an asset is used up or a liability is incurred. In terms of the accounting equation, expenses reduce owners' equity.
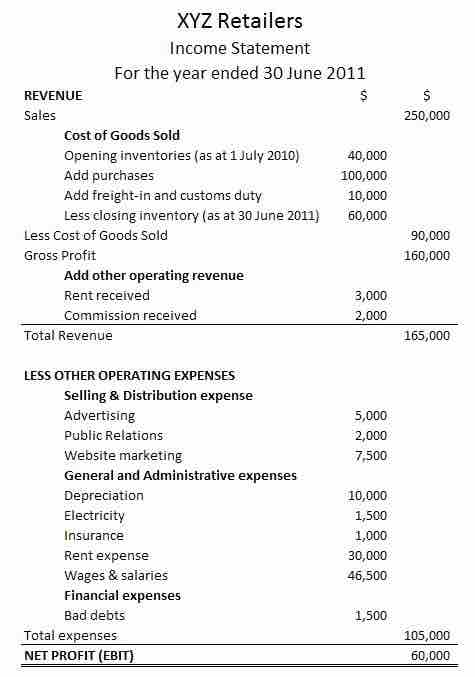
A Sample Income Statement
Expenses are listed on a company's income statement.
The International Accounting Standards Board defines expenses as follows: "Expenses are decreases in economic benefits during the accounting period in the form of outflows or depletions of assets or incurrences of liabilities that result in decreases in equity, other than those relating to distributions to equity participants. "
An important issue in accounting is when to recognize expenditures. When a business recognizes an expenditure, it records the amount in its financial records. The expenditure offsets the income the business earned and is used to calculate the business's profit.
This makes the timing of expenses and revenues very important. By shifting the timing of when expenses are recognized, a company can artificially make its business appear more profitable. Therefore, the accounting standards institute has established clear guidelines to minimize any subjective judgment regarding when to recognize expenses. Thus, the accounting method the business uses depends on when an expense is recognized.
Cash Basis Accounting
If the business uses cash basis accounting, an expenditure is recognized when the business pays for a good or service. Generally, cash basis accounting is reserved for tax accounting, not for financial reports.
Accrual Basis Accounting
Most financial reporting in the US is based on accrual basis accounting. Under the accrual system, an expense is not recognized until it is incurred. This means it is unimportant with regard to recognition when a business pays cash to settle an expense.