Access 2000
Queries
Introduction
By the end of this lesson, learners should be able to:
- Define a query
- Run an existing query
- Create a Simple Select query
What is a Query?
In the preceding Access 2000 lessons, you learned to work with database objects such as tables and forms. A query is another type of database object.
A query is data resulting from questions you ask of one or more tables. For example, let's say you want to find out how many male students are in Mr. Emerson's class.
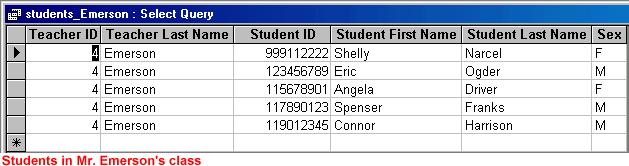
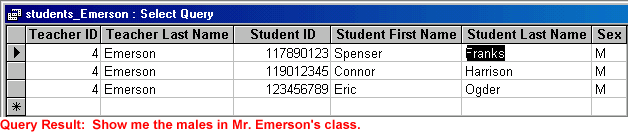
Run an Existing Query
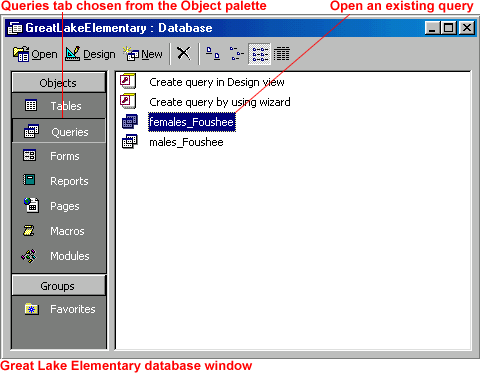
To Run an Existing Query:
- Open the Great Lake Elementary database.
- In the database window, choose the Queries tab from the Object palette.
- To open a query, double-click the title, select the title and click the
Open button,
 or right-click the title and choose Open from the shortcut menu.
or right-click the title and choose Open from the shortcut menu.
Creating a Simple Query
To Create a Simple Query:
- Open the Great Lake Elementary database.
- In the database window, choose the Queries tab from the Object palette.
- Select
 and click the Open button,
and click the Open button,  double-click it, or right-click it and choose Open from the shortcut menu.
double-click it, or right-click it and choose Open from the shortcut menu.
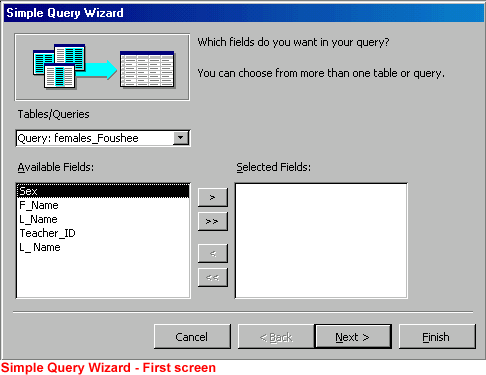
- The Simple Query Wizard opens.
- From the Tables/Queries drop-down list, choose the table/query containing the fields you want to include in the query.
- In the Available Fields text box, select the fields you want to include and click the right arrow or double-click the field to move the fields into the Selected Fields text box.
- Select any additional tables/queries from the Tables/Queries drop down list and repeat. Click Next when all fields have been selected.
- If the fields you selected include a number field, you're asked to select a summary or detail query. To see each record, choose Detail. To see sums, averages, etc, choose Summary and set the summary options. Click Next.
- Provide a name for the query. Click Finish to run the query.
Sorting, Finding, and Filtering Query Results
You can sort, find, and filter the results of a query just as you would other records. See Access 2000 lessons 9-12 for further details.
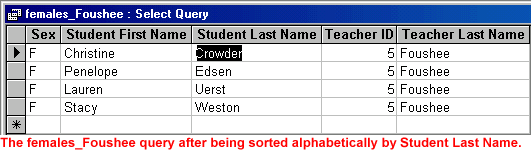
When you sort a query, and then close it, you are asked if you wish to save the changes to the query design. If you save the changes, the query will still be sorted the next time you open it. If you choose not to save changes, the query returns to the original order.
If you filtered a query and know you want to re-use it, remember to apply the filter just before closing it. Access will ask if you want to save changes to the design of the query. If you answer yes to save changes, the last filter is saved. When you open the form again, ALL records will be visible. To view your filter, click the Apply Filter button to reapply the filter. However, Access only saves the last filter you create.
Challenge!
- Open the Great Lake Elementary database.
- Choose Queries from the Object palette.
- Open the males_Emerson query and sort the query result alphabetically by Student Last Name.
- Close the query and choose not to save changes.


