This isn't so much a "how to troubleshoot" as it is "the most likely problem based on your description", but have you installed the private key as well as the client certificates?
In your browser's key store (which, for IE or Chrom[e|ium] on Windows, is the Windows key store), make sure that both the client certificate and its corresponding private key are installed.
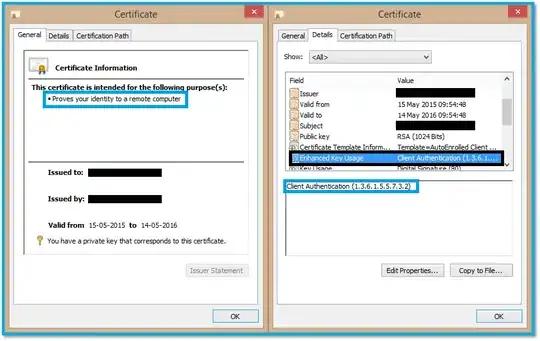
If you look at the certificate in the Certificate Manager GUI (use Start search and/or launch certmgr.msc; you probably want the "User Certificates" store, not the system one), there should be a little key icon in the upper left of the certificate icon (the cert icon by itself being a rectangle with a little ribbon in the lower right), and when you open the certificate, it should again have a little key icon in the bottom of the General tab, and say "You have a private key that corresponds to this certificate."
If it doesn't, the certificate is unusable as a client certificate. Just like the server needs the private key for its certificate when it presents it to the browser, the browser needs the private key for its certificate when it presents it to the server. Without the private key, the browser will not display the cert as an option for the TLS mutual authentication.
To fix this issue, go find the private key that the certificate was created with, and install it on your computer. It is likely to be bundled with the certificate in a .PFX or .P12 (or similar) file. If the certificate was exported from another machine, make sure it was exported with the private key (by default, Windows does not export the private key). If you cannot get the private key - if it's lost, or the passphrase for it is lost, or if it's marked non-exportable (and you don't want to do the rather hacky steps to export it anyhow) on the only machine where it's present - then you will need to create a new certificate signing request with a new key, and get the cert issued again.
Other possible reasons why the browser might not trust/present the certificate:
- It's outside its validity period (either expired, or not yet valid).
- To check, look at the "Valid from" box and also check the certificate Information box (it will say "This certificate has expired or is not yet valid.") Note that the cert in the screenshot has expired, but had not yet when the image was captured.
- To fix: Wait until it is valid (if not yet), or get the cert re-issued.
- It isn't marked as usable for client identification.
- To check: In the certificate information box, it will probably say "Proves your identity to a remote computer" (see the blue box on the left side of the screenshot) and in the Details tab, under Enhanced Key Usage, it should say "Client Authentication" along with a long series of dots and numbers called an OID.
- To fix: Get the cert re-issued with the right OID(s).
- Its signature is invalid. The certificate was tampered with after it was issued, without being re-signed.
- To check: Windows will say that the certificate's signature is invalid, probably both in the Certificate Information box (General tab) and the Certificate Status box (Certification Path tab).
- To fix: Go back to the original certificate file as issued by the CA (or as originally self-signed, if it's a self-signed cert), or get it re-issued.
- The certificate's signature cannot be validated. This happens if the certificate is issued by a CA (Certificate Authority) whose public key is not installed on your computer.
- To check: The Certificate Information box will say "Windows cannot verify the certificate's signature" or anything like that, and look at the Certification Path tab to see which certificate in the chain Windows is looking for but not finding.
- To fix: Download and install the CA's certificate (you do not need, and probably shouldn't have access to, the CA's private key). Note that if Windows doesn't recognize the CA automatically, there's a good chance that your HTTPS server won't, either.
- Some certificate in the certification chain is revoked, expired, or otherwise invalid.
- To check: The certificate information box will say "Windows cannot verify the authenticity of this certificate" or similar. Look at the certification path to see which cert in the chain is invalid; it'll have a little red (X) in the corner of its icon.
- To fix: Download and install the CA's new or correct certificate. If the public key was changed, you will also need to replace any certificates which were issued using the old key, which may mean needing to get your cert re-issued.
Hope that helps!
