In the United States, states are guaranteed military and civil defense by the federal government. The federal government is also required to ensure that the government of each state remains a republic. Four states use the official name of Commonwealth, rather than State. However, this is merely a paper distinction. The United States Constitution uniformly refers to all of these sub-national jurisdictions as States .
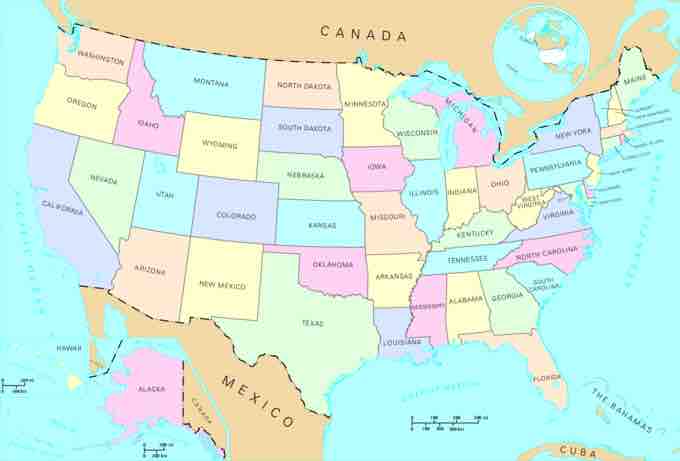
The United States
Americans live in a federal system of 50 states that, together, make up the United Sates of America.
Under Article Four of the United States Constitution, which outlines the relationship between the states, the United States Congress has the power to admit new states to the Union. The Article imposes prohibitions on interstate discrimination that are central to our status as a single nation. The states are required to give full faith and credit to the acts of each other's legislatures and courts, which is generally held to include the recognition of legal contracts, marriages, criminal judgments, and before 1865, slavery status. States are prohibited from discriminating against citizens of other states with respect to their basic rights, under the Privileges and Immunities Clause. Under the Extradition Clause, a state must extradite people located there who have fled charges of treason, felony, or other crimes in another state if the other state requests extradition.
The Article contends that the Constitution grants Congress expansive authority to structure interstate relations and that in wielding this interstate authority Congress is not limited by judicial interpretations of Article 4. The provisions are judicially enforceable against the states. However, the ability to enforce the provisions is dependent on the absence of congressionally authorized discrimination.