Section 5
Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy
By Boundless
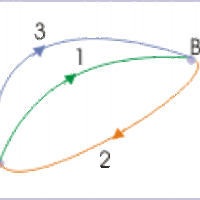
Conservative force—a force with the property that the work done in moving a particle between two points is independent of the path it takes.

Potential energy is the energy difference between the energy of an object in a given position and its energy at a reference position.

Gravitational energy is the potential energy associated with gravitational force, as work is required to move objects against gravity.
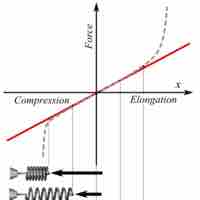
When a spring is stretched/compressed from its equilibrium position by x, its potential energy is give as
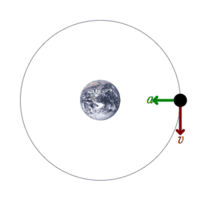
Conservation of mechanical energy states that the mechanical energy of an isolated system remains constant without friction.

To solve a conservation of energy problem determine the system of interest, apply law of conservation of energy, and solve for the unknown.
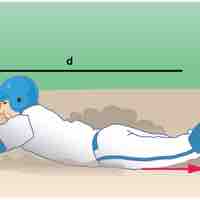
In the presence of dissipative forces, total mechanical energy changes by exactly the amount of work done by nonconservative forces (Wc).