Concept
Version 11
Created by Boundless
Nuclear Binding Energy and Mass Defect
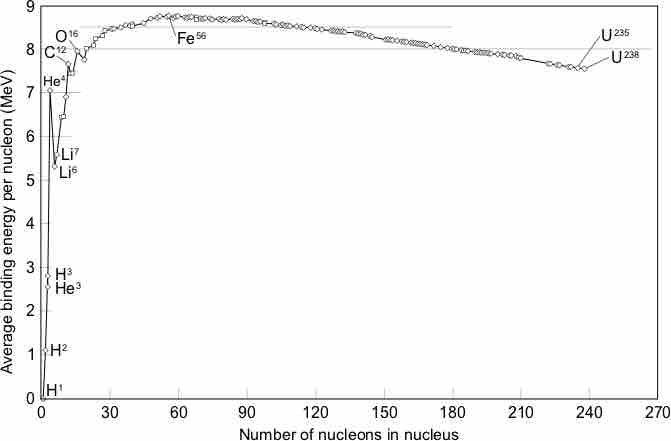
Nuclear binding energy curve
This graph shows the nuclear binding energy (in MeV) per nucleon as a function of the number of nucleons in the nucleus. Notice that iron-56 has the most binding energy per nucleon, making it the most stable nucleus.
Source
Boundless vets and curates high-quality, openly licensed content from around the Internet. This particular resource used the following sources:
"File:Binding energy curve - common isotopes.svg - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia."
http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=File:Binding_energy_curve_-_common_isotopes.svg&page=1
Wikipedia
Public domain.