Concept
Version 9
Created by Boundless
The Structure and Properties of Water
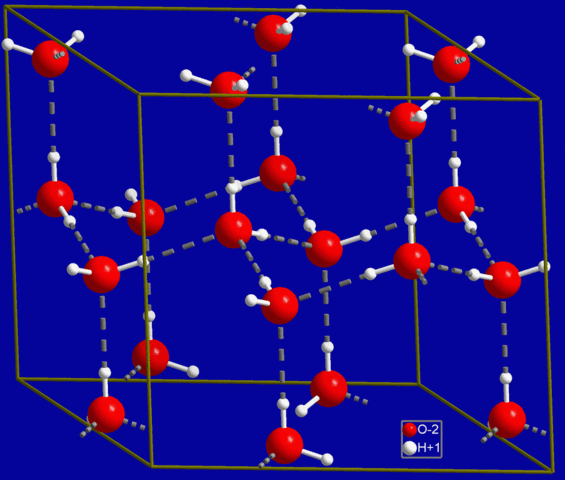
The hexagonal structure of ice
As a naturally occurring crystalline inorganic solid with an ordered structure, ice is considered to be a mineral. It possesses a regular crystalline structure based on the molecular structure of water, which consists of a single oxygen atom covalently bonded to two hydrogen atoms: H-O-H.
Source
Boundless vets and curates high-quality, openly licensed content from around the Internet. This particular resource used the following sources: