Genetic Drift
Effect of genetic drift
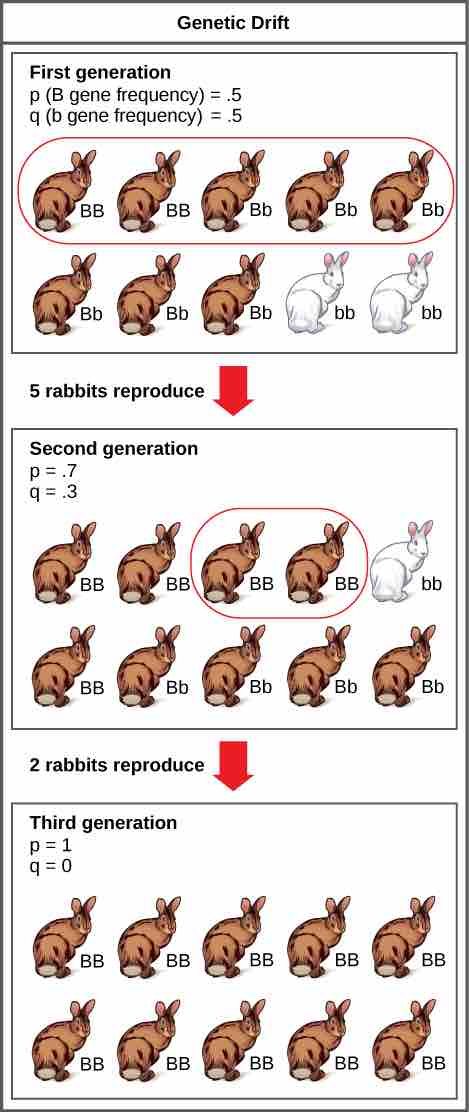
Genetic drift in a population can lead to the elimination of an allele from that population by chance. In this example, the brown coat color allele (B) is dominant over the white coat color allele (b). In the first generation, the two alleles occur with equal frequency in the population, resulting in p and q values of .5. Only half of the individuals reproduce, resulting in a second generation with p and q values of .7 and .3, respectively. Only two individuals in the second generation reproduce and, by chance, these individuals are homozygous dominant for brown coat color. As a result, in the third generation the recessive b allele is lost.
Source
Boundless vets and curates high-quality, openly licensed content from around the Internet. This particular resource used the following sources: