Concept
Version 7
Created by Boundless
Mosses
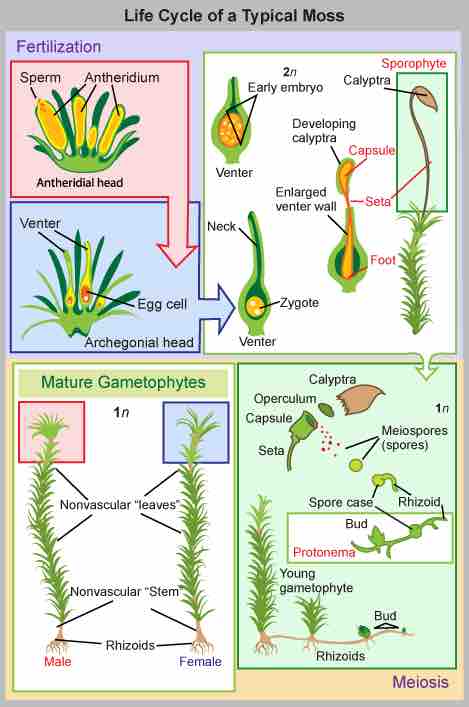
Life cycle of mosses
The alternation of generations cycle begins when the gametophyte germinates from a haploid spore and forms a protonema. Apical meristem-like cells divide and give rise to the gametophores. The archegonium (female organ) and antheridium (male organ) develop on separate gametophores. After fertilization, the zygote divides and grows into a sporophyte, which stays attached to the gametophyte. Spores released from the sporophyte germinate and produce gametophytes; the process begins again.
Source
Boundless vets and curates high-quality, openly licensed content from around the Internet. This particular resource used the following sources:
"OpenStax College, Bryophytes. October 17, 2013."
http://cnx.org/content/m44638/latest/Figure_25_03_06.png
OpenStax CNX
CC BY 3.0.