Modern politics in the United States is a two-party system dominated by the Democratic Party and the Republican Party. One of these two parties has won every United States presidential election since 1852 and has controlled the United States Congress since at least 1856.
Modern Two-Party System
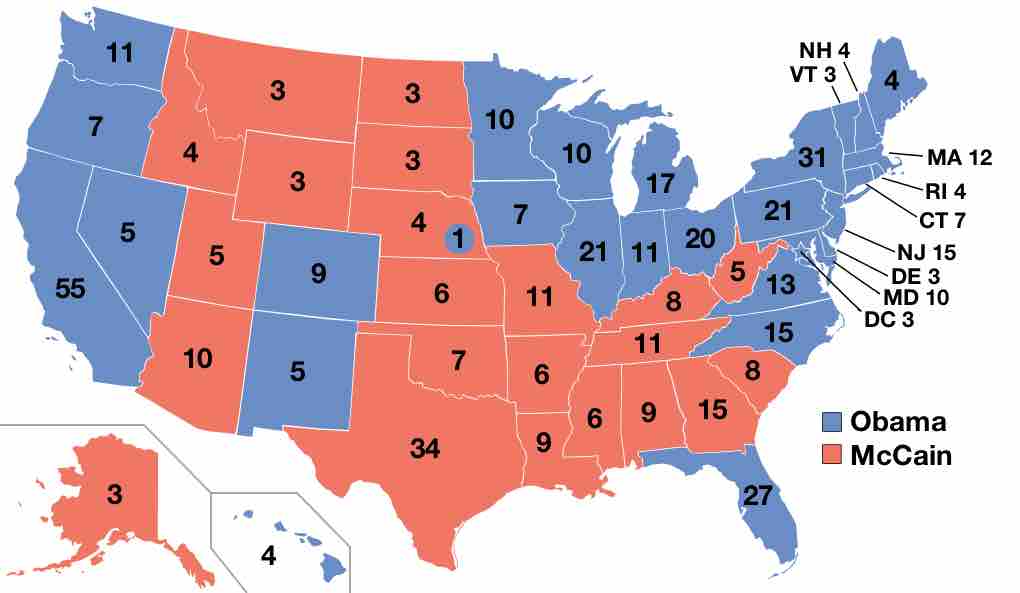
The 2008 elections, while won by a Democrat, reflect the relatively even divide in the United States between the Republican and Democratic Parties.
The Democratic Party is one of two major political parties in the United States, and is the oldest political party in the world. Since the division of the Republican Party in the election of 1912, it has positioned itself as progressive and supporting labor in economic as well as social matters. The economic philosophy of Franklin D. Roosevelt, which has strongly influenced American liberalism, has shaped much of the party's agenda since 1932, and Roosevelt's New Deal coalition controlled the White House until 1968.
In 2004, it was the larger major political party, with 72 million voters (42.6% of 169 million registered) claiming affiliation. The current President of the United States, Barack Obama, is the 15th Democrat to hold the office, and since the 2006 midterm elections, the Democratic Party has held a majority in the United States Senate.
A 2011 USA Today review of state voter rolls indicates that registered Democrats declined in 25 of the 28 states that register voters by party. Democrats were still the largest political party with more than 42 million voters (compared with 30 million Republicans and 24 million independents). However, in 2011, the number of Democrats shrank 800,000, and from 2008 they were down by 1.7 million, or 3.9%.
The other major contemporary political party in the United States is the Republican Party. It is often referred to as the GOP, which stands for "Grand Old Party," or "Gallant Old Party". Founded in 1854 by Northern anti-slavery expansion activists and modernizers, the Republican Party rose to prominence with the election of Abraham Lincoln, the first Republican to campaign on the Northern principles of anti-slavery. The party presided over the American Civil War and Reconstruction but was harried by internal factions and scandals toward the end of the 19th century. Today, the Republican Party supports an American conservative platform, with foundations in economic liberalism, fiscal conservatism, and social conservatism.
Former President George W. Bush was the 19th Republican to hold that office. The party's nominee for President of the United States in the 2012 presidential election is former Massachusetts Governor Mitt Romney. Since the 2010 midterm elections, the Republicans have held a majority in the United States House of Representatives.
USA Today's review of state voter rolls indicates that registered Republicans declined in 21 of the 28 states that register voters by party, and that Republican registrations were down 350,000 in 2011. The number of independents rose in 18 states, increasing by 325,000 in 2011, and was up more than 400,000 from 2008, or 1.7%.