Women's participation in the workforce has been a relatively recent phenomenon. Until modern times, legal and cultural practices, combined with the inertia of longstanding religious and educational conventions, restricted women's entry and participation in the workforce.
Particular barriers to equal participation in the workplace included a lack of access to educational opportunities; prohibitions or restrictions on members of a particular gender entering a field or studying a field; discrimination within fields, including wage, management, and prestige hierarchies; and the expectation that mothers, rather than fathers, should be the primary childcare providers.
Within the United States, World War I and World War II provided many new opportunities for women to participate in the workplace, including jobs as secretaries, salespeople, factory workers. Beginning in the 1970s, women began attending colleges and graduate schools in large numbers and entering professions like law, medicine, and business. Many scholars attribute this trend to the advent of the birth control pill, which allowed women to postpone pregnancy and marriage and focus instead on their education and careers. This transformation of women's expectations had a profound effect on their conception of their own identity and still continues on today.
Challenges that remain for women in the workplace include the gender pay gap, the difference between women's and men's earnings due to lifestyle choices and explicit discrimination; the "glass ceiling", which prevents women from reaching the upper echelons within their companies; sexism and sexual harassment; and network discrimination, wherein recruiters for high-status jobs are generally men who hire other men.
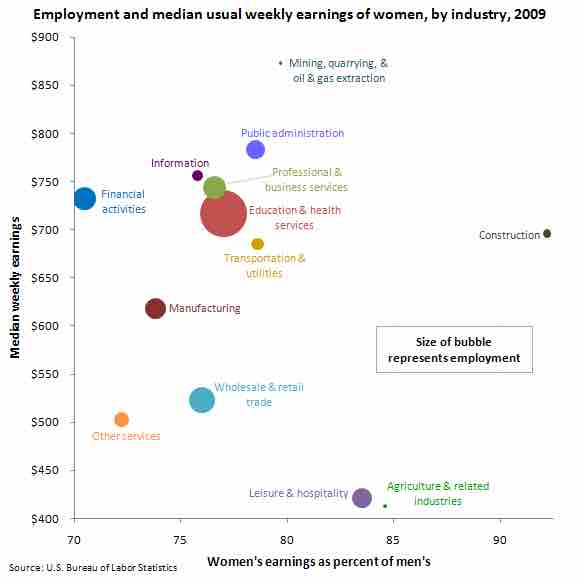
Gender pay gap
A chart depicting women's earnings in different industries as a percentage of men's earnings