Concept
Version 13
Created by Boundless
Regulation of Urine Concentration and Volume
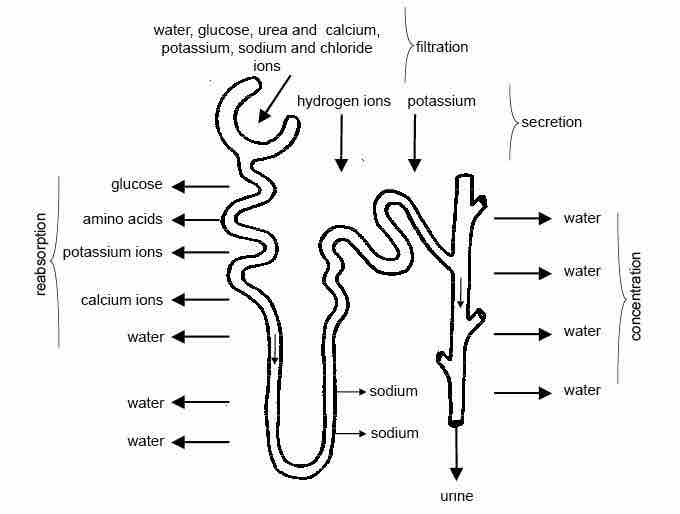
Summary of the process of urine formation
As the fluid flows along the proximal convoluted tubule useful substances like glucose, water, salts, potassium ions, calcium ions, and amino acids are reabsorbed into the blood capillaries that form a network around the tubules. Many of these substances are transported by active transport and energy is required.
This is a diagram of the process of urine formation. As the fluid flows along the proximal convoluted tubule useful substances like glucose, water, salts, potassium ions, calcium ions, and amino acids are reabsorbed into the blood capillaries that form a network around the tubules. Many of these substances are transported by active transport and energy is required.
Source
Boundless vets and curates high-quality, openly licensed content from around the Internet. This particular resource used the following sources:
"Anatomy and physiology of animals Summary of the processes involved in the formation of urine."
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Anatomy_and_physiology_of_animals_Summary_of_the_processes_involved_in_the_formation_of_urine.jpg
Wikimedia
CC BY-SA 3.0.