Calcium metabolism or calcium homeostasis is the mechanism by which the body maintains adequate calcium levels. Derangements of this mechanism lead to hypercalcemia or hypocalcemia, both of which can have important consequences for health.
Although calcium flow to and from the bone is neutral, about five mmol is turned over a day. Bone serves as an important storage point for calcium, as it contains 99% of the total body calcium. Calcium release from bone is regulated by parathyroid hormone. Calcitonin stimulates incorporation of calcium in bone.
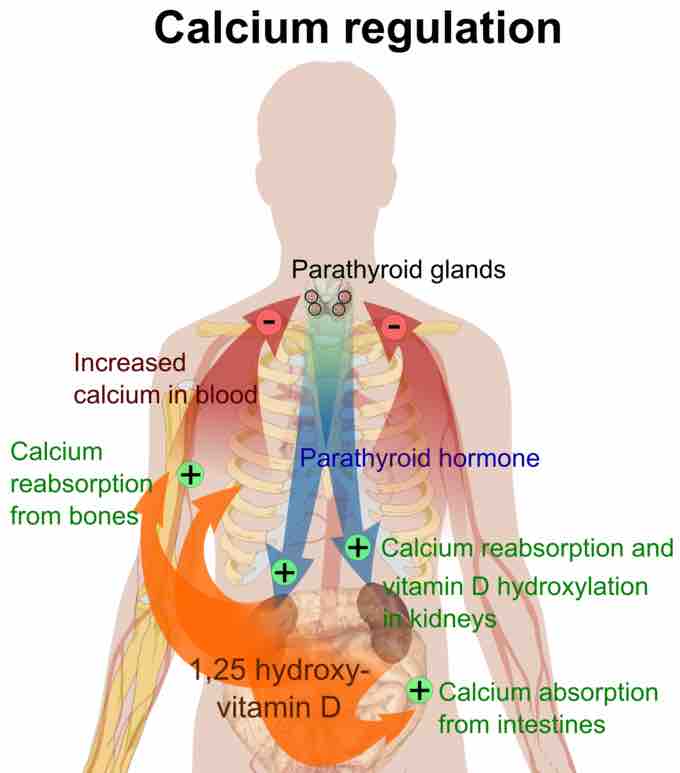
Calcium regulation
Parathyroid hormone regulates the levels of calcium in the blood.
Low calcium intake may be a risk factor in the development of osteoporosis. With a better bone balance, the risk of osteoporosis is lowered. Supplementation with vitamin D and calcium slightly improves bone mineral density.
Vitamin D and Calcium Homeostasis
Vitamin D is converted to calcidiol in the liver. Part of the calcidiol is converted by the kidneys to calcitriol, the biologically active form of vitamin D. It circulates as a hormone in the blood, regulating the concentration of calcium and phosphate in the bloodstream and promoting the healthy growth and remodeling of bone.
Responses to Blood Calcium Changes
The process of bone resorption by the osteoclasts releases stored calcium into systemic circulation and is an important process for regulating calcium balance. As bone formation actively fixes circulating calcium in its mineral form by removing it from the bloodstream, resorption actively unfixes it, thereby increasing circulating calcium levels.
When blood calcium concentration rises, the parafollicular cells of the thyroid gland increase calcitonin secretion into the blood. At the same time, the parathyroid glands reduce parathyroid hormone secretion into the blood. The resulting high levels of calcitonin in the blood stimulate the bone to remove calcium from the blood plasma and deposit it as bone.
Removal of calcium from the bone is also inhibited. When the blood calcium level is too low, calcitonin secretion is inhibited and PTH secretion is stimulated. This results in the removal of calcium from the bone to correct blood calcium levels.