Neuroglia in the CNS include astrocytes, microglial cells, ependymal cells and oligodendrocytes. In the human brain, it is estimated that the total number of glia roughly equals the number of neurons, although the proportions vary in different brain areas.
Astrocytes are star shaped delicate branching glial cells. Their numerous radiating processes cling to neurons and their synaptic endings. These astrocytes cover nearly all the capillaries in the CNS. They support and brace the neurons and anchor them to their nutrient supply lines. They also play an important role in making exchanges between capillaries and neurons. They also regulate the external chemical environment of neurons by removing excess ions and recycling neurotransmitters released during synaptic transmission.
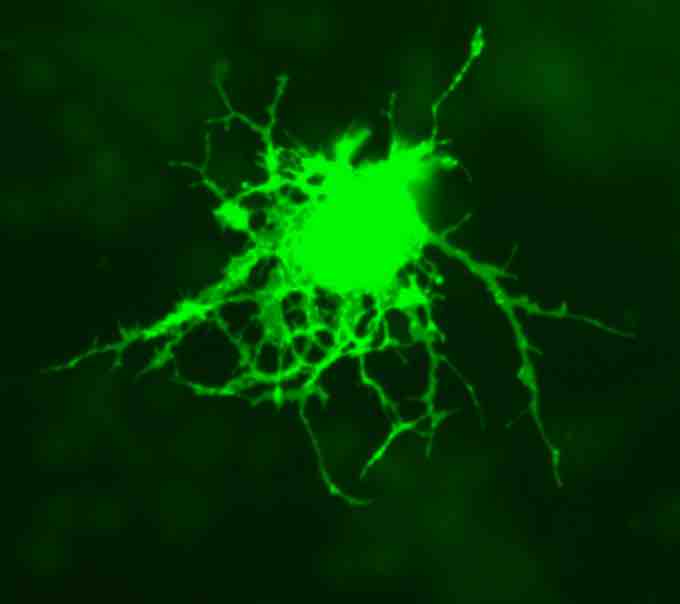
Oligodendrocyte
Oligodendrocytes form the electrical insulation around the axons of CNS nerve cells.
Microglial cells are small and have thorny processes that can touch the neighboring neurons. Microglial cells can transform into a special type of macrophage that can clear up the neuronal debris. They are also able to monitor the health of neurons by detecting injuries to the neuron.
Ependymal cells are another glial subtype that line the ventricles of the CNS. These cells line the cavities where they form a permeable barrier between the CSF and tissues fluid bathing the CSF. The beating of their cilia helps to circulate the CSF.
Oligodendrocytes are cells that have fewer processes compared to astrocytes. They line up along the nerve fibers in the CNS and wrap their process tightly around the fibers producing an insulating covering called myelin sheath.