Grey Matter
The basic pattern of the CNS is a central cavity surrounded by gray matter external to which is the white matter. The spinal cord exhibits this basic pattern, but the brain has additional regions of gray matter not present in the spinal cord. Both the cerebrum and cerebellum have an outer additional layer of gray matter.
Gray matter is a major component of the central nervous system, consisting of neuronal cell bodies. Grey matter is distributed at the surface of the cerebral hemispheres and cerebellum, as well as in the depths of the cerebrum, cerebellar, brainstem, and spinal grey matter.
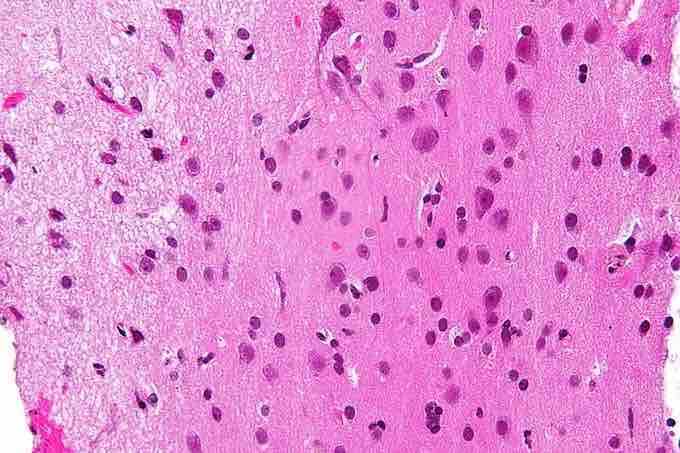
Grey and White Matter
Micrograph showing grey matter, with the characteristic neuronal cell bodies (right of image - darker pink), and white matter with its characteristic fine mesh work-like appearance (left of image - lighter pink).
White Matter
A second major component of the central nervous system is white matter and it is composed of bundles of myelinated axons that connect various grey matter regions of the nervous system to each other and carry nerve impulses between neurons . White matter only contains the myelinated axon tracts, and not the cell bodies. Myelin is a lipid that forms a thin layer, known as the myelin sheath, around the axons. It acts as an electrical insulator and increases speed of transmission by allowing the signal to jump down the axon. Myelin also gives white matter its characteristic color.
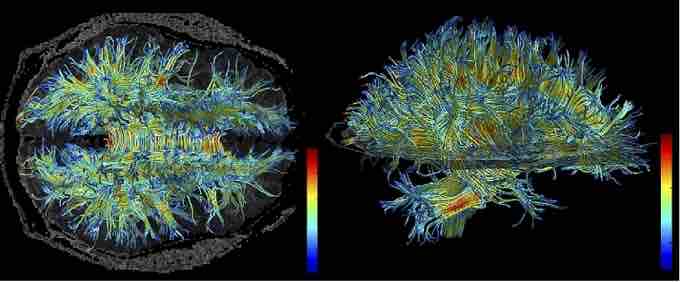
White Matter on an MRI
This MRI highlights the location of white matter in the brain.