Concept
Version 8
Created by Boundless
Lipids: Sources, Uses in the Body, and Dietary Requirements
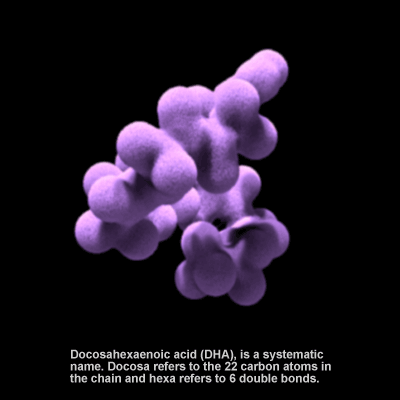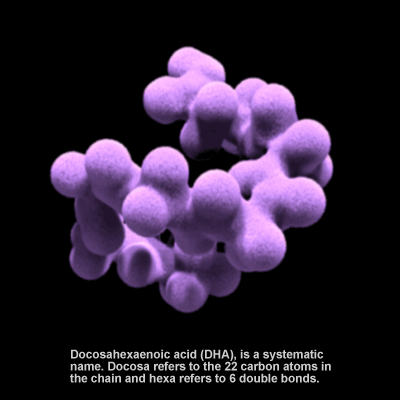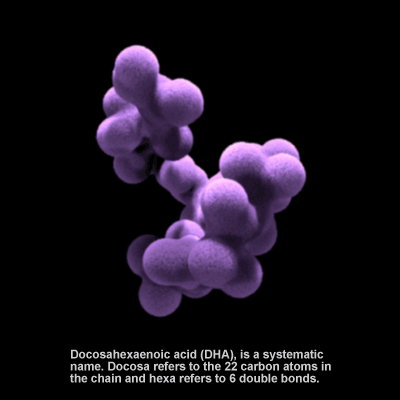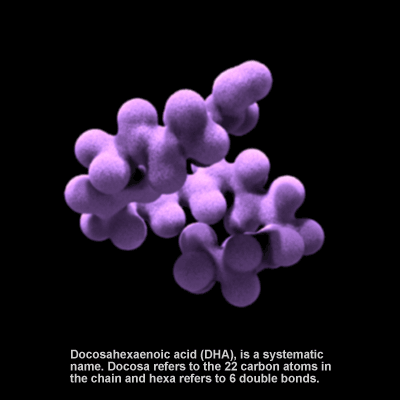
Omega-3 Fatty Acid
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is an omega-3 fatty acid. It is essential for proper functioning of the brain in both adults and infants. DHA concentrations in breast milk range from 0.07-1.0% of total fatty acids and are influenced by the amount of fatty fish in the mother's diet. In the U.S., infant formula has been supplemented with DHA since 2001. Research suggests that DHA contributes to numerous nervous system functions such as visual acuity, neurogenesis, and synaptogenesis, and that it lowers the risk for cardiovascular disease. It is highly concentrated in the brain and eye.
Source
Boundless vets and curates high-quality, openly licensed content from around the Internet. This particular resource used the following sources: