In mammals, the adrenal glands (also known as the suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that sit atop the kidneys. They are chiefly responsible for releasing three classes of hormones:
- Mineralocorticoids (aldosterone)
- Glucocorticoids (cortisol)
- Androgens (DHEA)
Along with catecholamines (adrenaline), these hormones control a variety of functions including kidney function, metabolism, fight-or-flight response, and sex hormone levels.
In humans, the adrenal glands are found at the level of the 12th thoracic vertebra sitting above and slightly medial to the kidneys, lying within the renal fascia, and separated from the kidneys by a thin layer of connective tissue. In humans, the right adrenal gland is triangular shaped, while the left adrenal gland is semilunar shaped.
Each adrenal gland has two distinct structures, the outer adrenal cortex and the inner medulla—both produce hormones. The cortex mainly produces mineralcorticoids, glucocorticoids, and androgens, while the medulla chiefly produces adrenaline and nor-adrenaline.
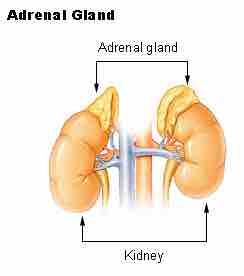
Adrenal glands
The adrenal glands are triangular-shaped organs on top of the kidneys.