Two venae cavae return deoxygenated blood from the systemic circulation to the right atrium of the heart.
The superior vena cava, formed from the left and right brachiocephalic veins, returns deoxygenated blood from the upper half of the body and carries blood from the upper limbs, head, and neck via the thyroid and jugular veins. It is joined just before entering the heart by the azygos vein, which runs up the right side of the thoracic vertebral column and transports blood from the external thoracic cavity.
The internal thoracic vein is a vessel that drains the chest wall and breasts. Bilaterally, it arises from the superior epigastric vein, accompanies the internal thoracic artery along its course, and terminates in the brachiocephalic vein.
The supreme intercostal vein is a paired vein that drains the first intercostal space on its corresponding side. It usually drains into the brachiocephalic vein.
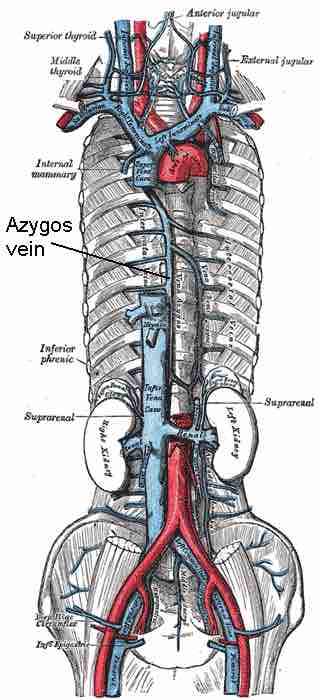
Veins of the Thorax
The veins of the thorax are shown in blue.
The inferior vena cava returns blood from the abdomen and lower limbs to the right atrium of the heart. The renal veins from the kidney and hepatic veins of the liver drain directly into the inferior vena cava. Additionally, the superior and inferior phrenic veins drain the diaphragm and usually open into the internal mammary vein and inferior vena cava, respectively.