Concept
Version 10
Created by Boundless
Adrenergic Neurons and Receptors
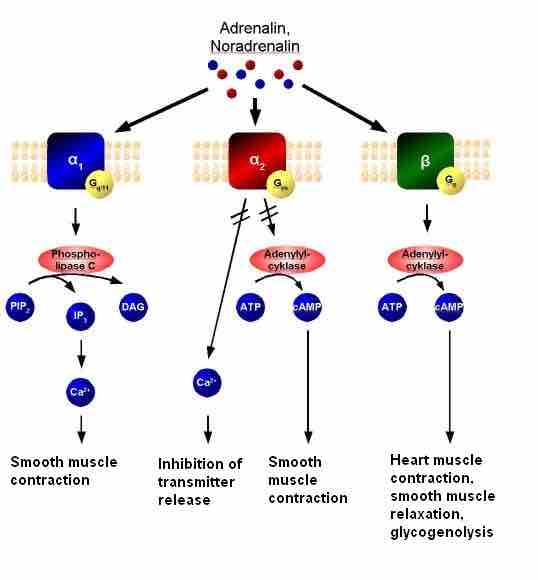
Adrenergic signal transduction
This schematic shows the mechanism of adrenergic receptors. Adrenaline and noradrenaline are ligands to α1, α2, or β-adrenergic receptors. α1-receptors couple to Gq, resulting in increased intracellular Ca2+ and causing smooth muscle contraction. α2 receptors couple to Gi, causing a decrease in cAMP activity and resulting in smooth muscle contraction. β-receptors couple to Gs, increasing intracellular cAMP activity and resulting in heart muscle contraction, smooth muscle relaxation, and glycogenolysis.
This schematic shows the mechanism of adrenergic receptors. Adrenaline and noradrenaline are ligands to α1, α2, or β-adrenergic receptors. α1 receptors couple to Gq, resulting in increased intracellular Ca2+ and causing smooth muscle contraction. α2 receptors couple to Gi, causing a decrease in cAMP activity and resulting in smooth muscle contraction. β receptors couple to Gs, increasing intracellular cAMP activity and resulting in heart muscle contraction, smooth muscle relaxation and glycogenolysis.
Source
Boundless vets and curates high-quality, openly licensed content from around the Internet. This particular resource used the following sources: