Characteristics of Waves
Waves have certain characteristic properties which are observable at first notice. The first property to note is the amplitude. The amplitude is half of the distance measured from crest to trough. We also observe the wavelength, which is the spatial period of the wave (e.g. from crest to crest or trough to trough). We denote the wavelength by the Greek letter
The frequency of a wave is the number of cycles per unit time -- one can think of it as the number of crests which pass a fixed point per unit time . Mathematically, we make the observation that,
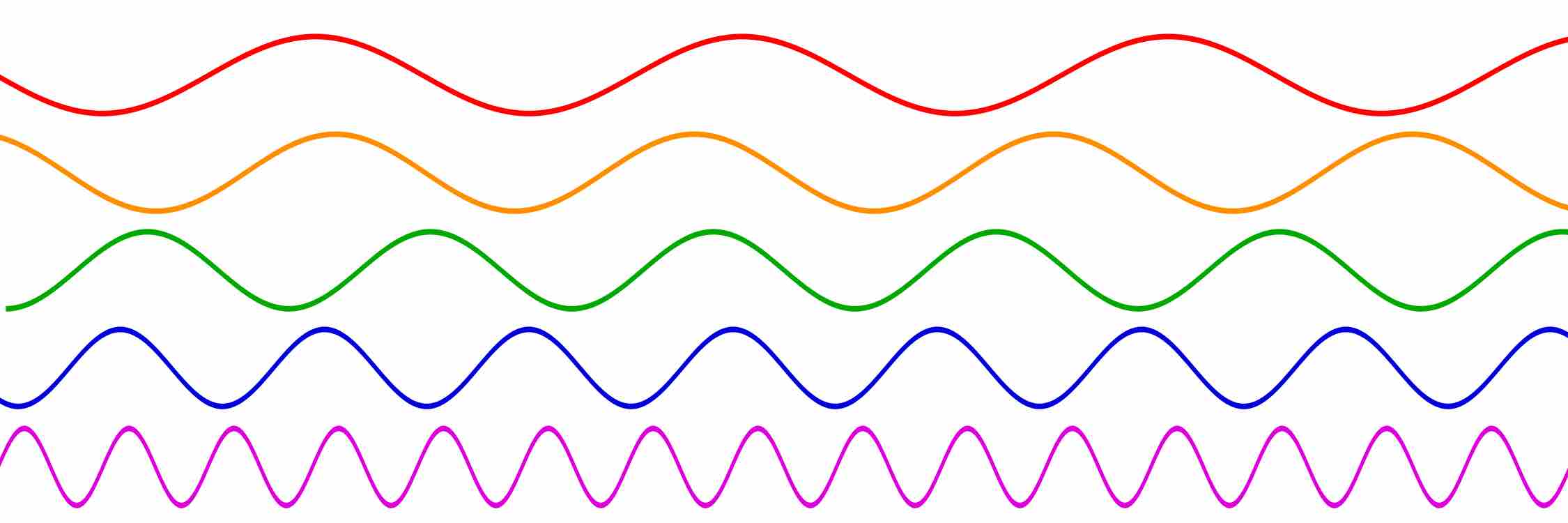
Frequencies of different sine waves.
The red wave has a low frequency sine there is very little repetition of cycles. Conversely we say that the purple wave has a high frequency. Note that time increases along the horizontal.
where T is the period of oscillation. Frequency and wavelength can also be related-* with respects to a "speed" of a wave. In fact,
where v is called the wave speed, or more commonly,the phase velocity, the rate at which the phase of the wave propagates in space. This is the velocity at which the phase of any one frequency component of the wave travels. For such a component, any given phase of the wave (for example, the crest) will appear to travel at the phase velocity.
Finally, the group velocity of a wave is the velocity with which the overall shape of the waves' amplitudes — known as the modulation or envelope of the wave — propagates through space. In , one may see that the overall shape (or "envelope") propagates to the right, while the phase velocity is negative.

Fig 2
This shows a wave with the group velocity and phase velocity going in different directions. (The group velocity is positive and the phase velocity is negative. )