Specific Heat
Heat Transfer and Specific Heat Capacity
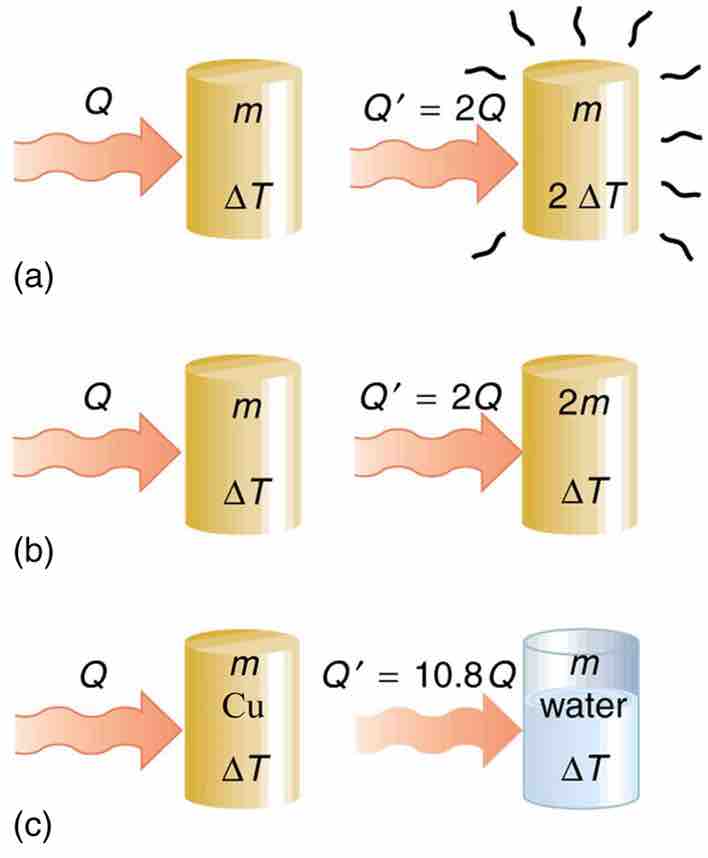
The heat Q transferred to cause a temperature change depends on the magnitude of the temperature change, the mass of the system, and the substance and phase involved. (a) The amount of heat transferred is directly proportional to the temperature change. To double the temperature change of a mass m, you need to add twice the heat. (b) The amount of heat transferred is also directly proportional to the mass. To cause an equivalent temperature change in a doubled mass, you need to add twice the heat. (c) The amount of heat transferred depends on the substance and its phase. If it takes an amount Q of heat to cause a temperature change ΔT in a given mass of copper, it will take 10.8 times that amount of heat to cause the equivalent temperature change in the same mass of water assuming no phase change in either substance.
Source
Boundless vets and curates high-quality, openly licensed content from around the Internet. This particular resource used the following sources: