The nervous system has three overlapping functions. These functions are based on the sensory input, integration and motor output. The nervous system is a highly integrated system.
Sensory input is based on the many sensory receptors that can monitor changes occurring both inside and outside the body. The total sum of the gathered information by these sensory receptors is called sensory input. Nervous system processes and interprets sensory input and decides what should be done at the each moment. The nervous system activates effector organs such as muscles and glands to cause a response called the motor input.
At a more integrative level, the primary function of the nervous system is to control and communicate information throughout the body. It does this by extracting information from the environment using sensory receptors. These sensory input is sent into the central nervous system which has the ability to determine an appropriate response. Once the response is activated, the nervous system is able to send signals via motor output to muscles or glands to initiate the response.
In humans, the sophistication of the nervous system makes it possible to have language, abstract representation of concepts, transmission of culture, and many other features of human society that would not exist without the human brain.
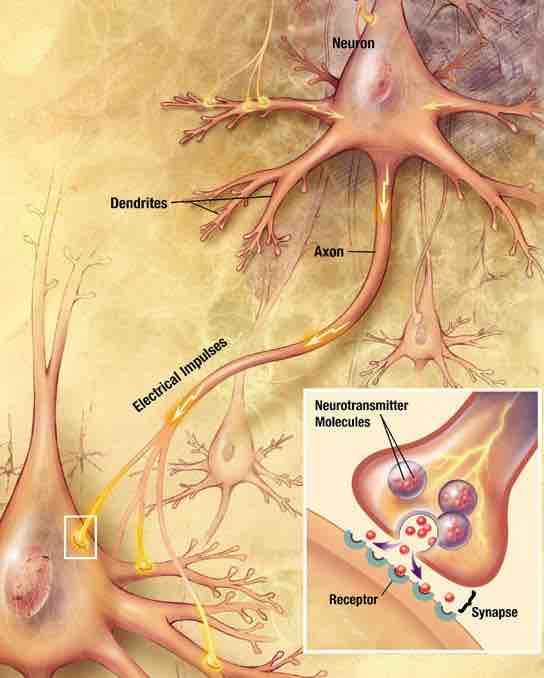
Major elements in neuron-to-neuron communication
Electrical impulses travel along the axon of a neuron. When this signal reaches a synapse, it provokes release of neurotransmitter molecules, which bind to receptor molecules located in the the target cell.