The Genitourinary Microbiome
The human microbiome, or human microbiota, is the aggregate of microorganisms that reside on the surface and in deep layers of skin, in the saliva and oral mucosa, in the conjunctiva, and in the gastrointestinal tracts. They include bacteria, fungi, and archaea. Some of these organisms perform tasks that are useful for the human host. However, the majority have no known beneficial or harmful effect. Those that are expected to be present and that under normal circumstances do not cause disease, but instead participate in maintaining health, are deemed members of the normal flora.
Populations of microbes inhabit the skin and mucosa. Their role forms part of normal, healthy human physiology; however, if microbe numbers grow beyond their typical ranges (often due to a compromised immune system) or if microbes populate atypical areas of the body (such as through poor hygiene or injury), disease can result.
Proportions of Microbes
It is estimated that 500 to 1000 species of bacteria live in the human gut and a roughly similar number on the skin. Bacterial cells are much smaller than human cells, and there are at least ten times as many bacteria as human cells in the body (approximately 1014 versus 1013). Normal flora bacteria can act as opportunistic pathogens at times of lowered immunity.The vaginal microflora consist mostly of various lactobacillus species . It was long thought that the most common of these species was Lactobacillus acidophilus, but it has later been shown that the most common one is L. iners followed by L. crispatus. Other lactobacilli found in the vagina are L. jensenii, L. delbruekii and L. gasseri. Disturbance of the vaginal flora can lead to bacterial vaginosis.
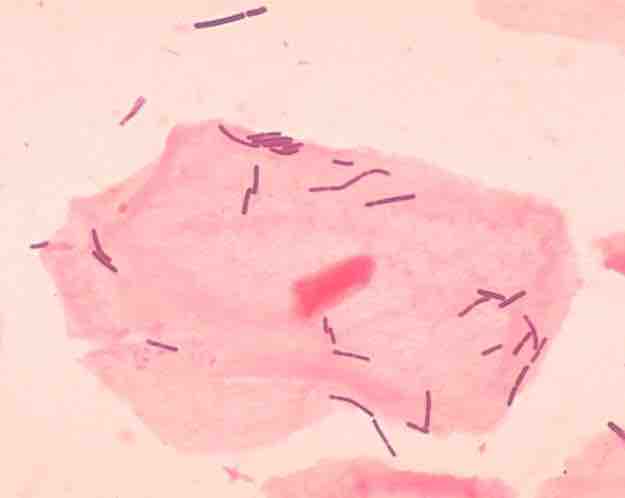
Lactobacillus
Lactobacilli and a vaginal squamous cell.