Chlamydia infection (from the Greek meaning "cloak") is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) in humans caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis . The term Chlamydia infection can also refer to infection caused by any species belonging to the bacterial family Chlamydiaceae. C. trachomatis is found only in humans.
Chlamydia
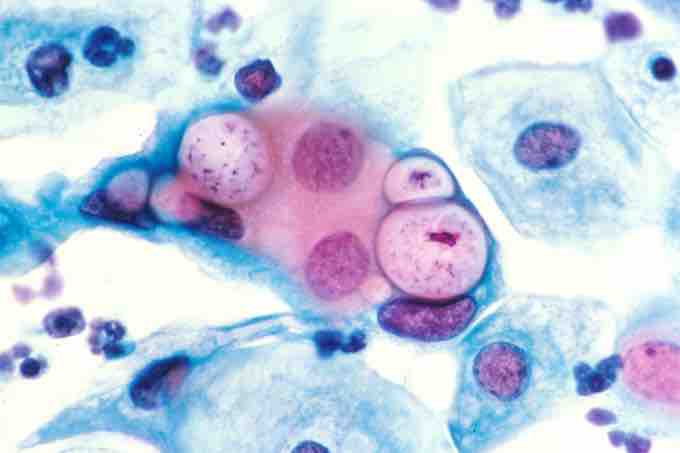
Pap smear showing C. trachomatis (H&E stain).
Chlamydia is a major infectious cause of human genital and eye disease. Chlamydia infection is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections worldwide; it is estimated that about 1 million individuals in the United States are infected with chlamydia. C. trachomatis is naturally found living only inside human cells. Chlamydia can be transmitted during vaginal, anal, or oral sex, and can be passed from an infected mother to her baby during vaginal childbirth. Between half and three-quarters of all women who have a chlamydia infection of the cervix (cervicitis) have no symptoms and do not know that they are infected. In men, infection of the urethra (urethritis) is usually symptomatic, causing a white discharge from the penis with or without pain on urinating (dysuria).
Occasionally, the condition spreads to the upper genital tract in women (causing pelvic inflammatory disease) or to the epididymis in men (causing epididymitis). If untreated, chlamydial infections can cause serious reproductive and other health problems with both short-term and long-term consequences.
Genital disease
Chlamydial cervicitis in a female patient characterized by mucopurulent cervical discharge, erythema, and inflammation. Male patients may develop a white, cloudy or watery discharge from the tip of the penis.
Women
Chlamydial infection of the neck of the womb (cervicitis) is a sexually transmitted infection which is asymptomatic for about 50-70% of women infected with the disease. The infection can be passed through vaginal, anal, or oral sex. Of those who have an asymptomatic infection that is not detected by their doctor, approximately half will develop pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), a generic term for infection of the uterus, fallopian tubes, and/or ovaries. PID can cause scarring inside the reproductive organs, which can later cause serious complications, including chronic pelvic pain, difficulty becoming pregnant, ectopic (tubal) pregnancy, and other dangerous complications of pregnancy.Chlamydia is known as the "Silent Epidemic" because in women, it may not cause any symptoms in 75% of cases, and can linger for months or years before being discovered. Symptoms that may occur include unusual vaginal bleeding or discharge, pain in the abdomen, painful sexual intercourse (dyspareunia), fever, painful urination or the urge to urinate more frequently than usual (urinary urgency).
Men
In men, chlamydia shows symptoms of infectious urethritis (inflammation of the urethra) in about 50% of cases. Symptoms that may occur include: a painful or burning sensation when urinating, an unusual discharge from the penis, swollen or tender testicles, or fever. Discharge, or the purulent exudate, is generally less viscous and lighter in color than for gonorrhea. If left untreated, it is possible for chlamydia in men to spread to the testicles causing epididymitis, which in rare cases can cause sterility if not treated within 6 to 8 weeks. Chlamydia is also a potential cause of prostatitis in men, although the exact relevance in prostatitis is difficult to ascertain due to possible contamination from urethritis.
Treatment
C. trachomatis infection can be effectively cured with antibiotics once it is detected. Current guidelines recommend azithromycin, doxycycline, erythromycin, or ofloxacin. Agents recommended for pregnant women include erythromycin or amoxicillin.
An option for treating partners of patients ( index cases ) diagnosed with chlamydia or gonorrhea is patient-delivered partner therapy (PDT or PDPT), which is the clinical practice of treating the sex partners of index cases by providing prescriptions or medications to the patient to take to his/her partner without the health care provider first examining the partner.