Section 1
Measuring Output Using GDP
By Boundless
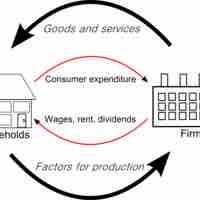
Gross domestic product is the market value of all final goods and services produced within the national borders of a country for a given period of time.

GDP is a measure of national income and output that can be used as a comparison tool.
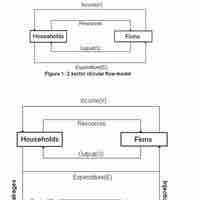
In economics, the "circular flow" diagram is a simple explanatory tool of how the major elements in an economy interact with one another.

GDP is the sum of Consumption (C), Investment (I), Government Spending (G) and Net Exports (X – M): Y = C + I + G + (X - M).
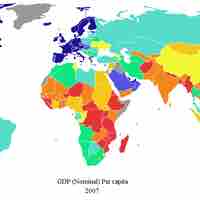
GDP can be calculated through the expenditures, income, or output approach.
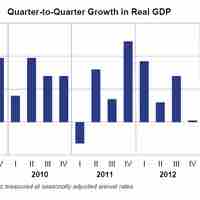
The income approach evaluates GDP from the perspective of the final income to economic participants.
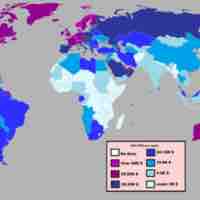
The value of GDP as a measure of the quality of life for a given country may be limited.