In economics, an externality is a cost or benefit resulting from an activity or transaction, that affects an otherwise uninvolved party who did not choose to be subject to the cost or benefit . An example of an externality is pollution. Health and clean-up costs from pollution impact all of society, not just individuals within the manufacturing industries. In regards to externalities, the cost and benefit to society is the sum of the value of the benefits and costs for all parties involved.
Externality
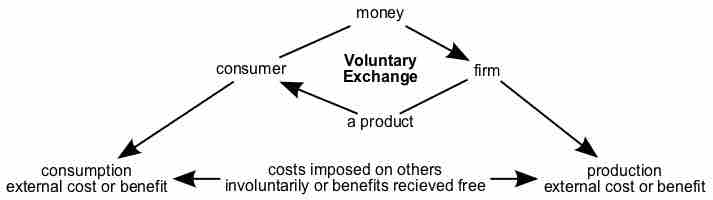
An externality is a cost or benefit that results from an activity or transaction and that affects an otherwise uninvolved party who did not choose to incur that cost or benefit.
Negative vs. Positive
A negative externality is an result of a product that inflicts a negative effect on a third party . In contrast, positive externality is an action of a product that provides a positive effect on a third party.

Negative Externality
Air pollution caused by motor vehicles is an example of a negative externality.
Externalities originate within voluntary exchanges. Although the parties directly involved benefit from the exchange, third parties can experience additional effects. For those involuntarily impacted, the effects can be negative (pollution from a factory) or positive (domestic bees kept for honey production, pollinate the neighboring crops).
Economic Strain
Neoclassical welfare economics explains that under plausible conditions, externalities cause economic results that are not ideal for society. The third parties who experience external costs from a negative externality do so without consent, while the individuals who receive external benefits do not pay a cost. The existence of externalities can cause ethical and political problems within society.
In regards to externalities, one way to correct the issue is to internalize the third party costs and benefits. However, in many cases, internalizing the costs is not financially possible. Governments may step in to correct such market failures.