Concept
Version 13
Created by Boundless
Modes of Radioactive Decay
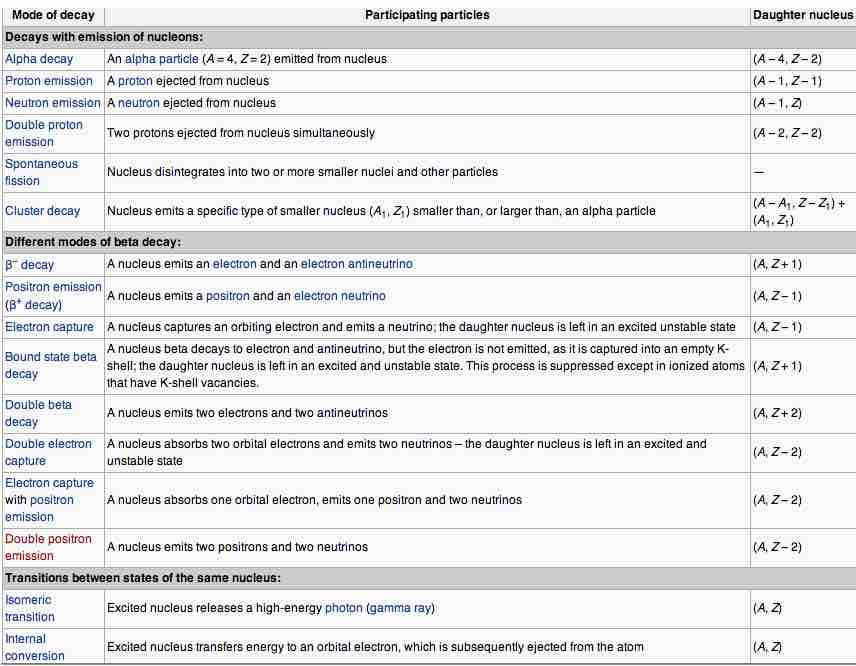
Table of modes of radioactive decay
Radionuclides can undergo a number of different reactions, summarized here. A nucleus with mass number A and atomic number Z is represented as (A, Z). The column "Daughter nucleus" indicates the difference between the new nucleus and the original nucleus. Thus, (A − 1, Z) means that the mass number is one less than before, but the atomic number didn't change.
Source
Boundless vets and curates high-quality, openly licensed content from around the Internet. This particular resource used the following sources: