Concept
Version 13
Created by Boundless
Electrolysis of Sodium Chloride
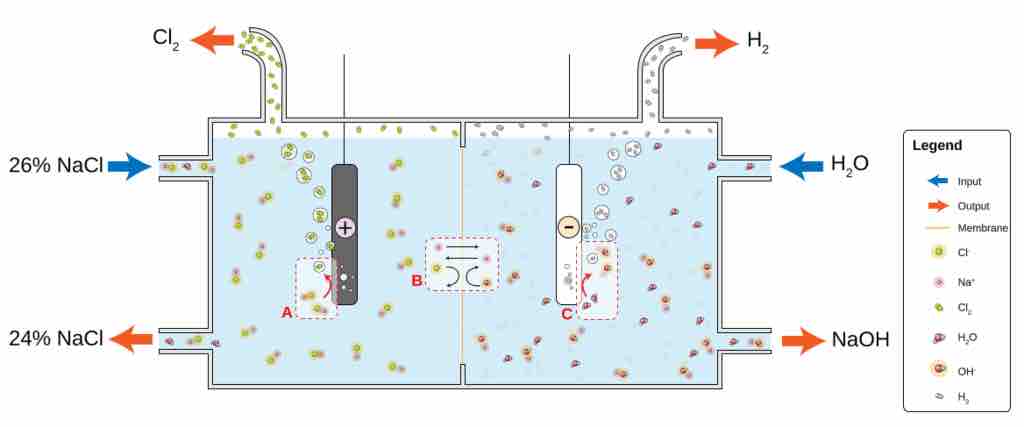
Electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride
Electrolysis of aqueous NaCl results in hydrogen and chloride gas. At the anode (A), chloride (Cl-) is oxidized to chlorine. The ion-selective membrane (B) allows the counterion Na+ to freely flow across, but prevents anions such as hydroxide (OH-) and chloride from diffusing across. At the cathode (C), water is reduced to hydroxide and hydrogen gas. The net process is the electrolysis of an aqueous solution of NaCl into industrially useful products sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and chlorine gas.
Source
Boundless vets and curates high-quality, openly licensed content from around the Internet. This particular resource used the following sources:
"Chloralkali_membrane.svg."
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Chloralkali_membrane.svg
Wikimedia
CC BY-SA 3.0.