The Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938 established a national minimum wage, forbade "oppressive" child labor, and provided for overtime pay in designated occupations. It declared the goal of assuring "a minimum standard of living necessary for the health, efficiency, and general well-being of workers." But it also allowed employers to replace striking workers.
Specifications
The standards apply to employees in the private sector and in Federal, State, and local governments. Covered nonexempt workers are entitled to a minimum wage of not less than $7.25 per hour effective July 24, 2009. Many states also have minimum wage laws, at a rate not less than one and one-half times the regular rate of pay is required after 40 hours of work in a workweek.
Covered nonexempt employees must receive for hours worked over 40 per workweek (any fixed and regularly recurring period of 168 hours — seven consecutive 24-hour periods) at a rate not less than one and one-half times the regular rate of pay. There is no limit on the number of hours employees 16 years or older may work in any workweek. The FLSA does not require [[#|overtime pay]] for work on weekends, holidays, or regular days of rest, unless overtime is worked on such days. Particular jobs may be completely excluded from coverage under the FLSA overtime rules. There are two general types of exclusion. Some jobs are specifically excluded in the statute itself. For example, employees of movie theaters and many agricultural workers are not governed by the FLSA overtime rules. Another type of exclusion is for jobs which are governed by some other specific federal. As a general rule, if a job is governed by some other federal, the FLSA does not apply. For example, most railroad workers are governed by the Railway Labor Act, and many are governed by the Motor Carriers Act, and not the FLSA.
Exempt or Nonexempt
Employees whose jobs are governed by the FLSA are either "exempt" or "nonexempt. " Nonexempt employees are entitled to overtime pay. Exempt employees are not. Most employees covered by the FLSA are nonexempt.
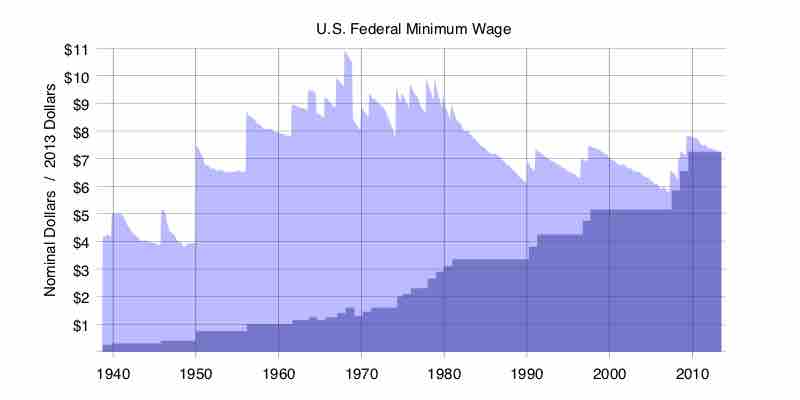
History of the Minimum Wage
This graph of the minimum wage in the United States shows the fluctuation in government guarantees for minimum standards of labor.