Organizational Ethics is how an organization ethically responds to an internal or external stimulus. Organizational ethics express the values of an organization to its employees and other entities, irrespective of governmental and/or regulatory laws. There are at least four elements that make ethical behavior conducive within an organization:
- A written code of ethics and standards
- Ethics training to executives, managers, and employees
- Availability for advice on ethical situations (i.e, advice lines or offices)
- Systems for confidential reporting.
Ethical Issues in Finance
The 2008 financial crisis caused critics to challenge the ethics of the executives in charge of U.S. and European financial institutions and regulatory bodies. Previously, finance ethics was somewhat overlooked because issues in finance are often addressed as matters of law rather than ethics. Fairness in trading practices, trading conditions, financial contracting, sales practices, consultancy services, tax payments, internal audits, external audits, and executive compensation also fall under the umbrella of finance and accounting. Specific corporate ethical/legal abuses include creative accounting, earnings management, misleading financial analysis, insider trading, securities fraud, bribery/kickbacks, and facilitation payments.
Ethical Issues in Human Resource Management
Human resource (HR) management involves recruitment selection, orientation, performance appraisal, training and development, industrial relations and health and safety issues. Discrimination by age (preferring the young or the old), gender, sexual orientation, race, religion, disability, weight, and attractiveness are all ethical issues that the HR manager must deal with.
Ethical Issues in Sales and Marketing
Ethics in marketing deals with the principles, values, and/or ideals by which marketers and marketing institutions ought to act. Ethical marketing issues include marketing redundant or dangerous products/services; transparency about environmental risks, product ingredients (genetically modified organisms), possible health risks, or financial risks; respect for consumer privacy and autonomy; advertising truthfulness; and fairness in pricing and distribution. Some argue that marketing can influence individuals' perceptions of and interactions with other people, implying an ethical responsibility to avoid distorting those perceptions and interactions.
Marketing ethics involves pricing practices, including illegal actions such as price fixing and legal actions including price discrimination and price skimming. Certain promotional activities have drawn fire, including greenwashing, bait-and-switch, shilling, viral marketing, spam (electronic), pyramid schemes, and multi-level marketing. Advertising has raised objections about attack ads, subliminal messages, sex in advertising, and marketing in schools.
Ethical Issues in Production
Business ethics usually deals with the duties of a company to ensure that products and production processes do not needlessly cause harm. Few goods and services can be produced and consumed with zero risk, so determining the ethical course can be problematic. In some cases, consumers demand products that harm them, such as tobacco products. Production may have environmental impacts, including pollution, habitat destruction, and urban sprawl. The downstream effects of technologies such as nuclear power, genetically modified food, and mobile phones may not be well understood. While the precautionary principle may prohibit introducing new technology whose consequences are not fully understood, that principle would have prohibited most of the new technology introduced since the industrial revolution. Product testing protocols have been attacked for violating the rights of both humans and animals.
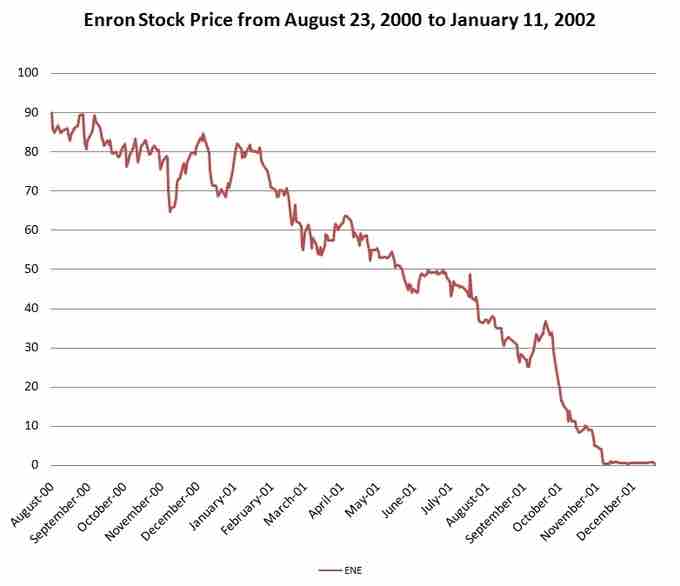
Enron Stocks During the 2001 Scandal
Enron's unethical practices led to their employees and shareholders losing billions of dollars as their stocks became worthless by November of 2001.