Gene Flow
An important evolutionary force is gene flow: the flow of alleles in and out of a population due to the migration of individuals or gametes. While some populations are fairly stable, others experience more movement and fluctuation. Many plants, for example, send their pollen by wind, insects, or birds to pollinate other populations of the same species some distance away. Even a population that may initially appear to be stable, such as a pride of lions, can receive new genetic variation as developing males leave their mothers to form new prides with genetically-unrelated females. This variable flow of individuals in and out of the group not only changes the gene structure of the population, but can also introduce new genetic variation to populations in different geological locations and habitats.
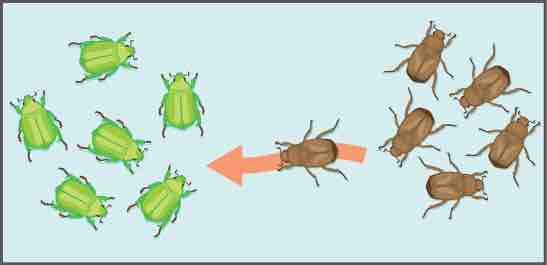
Gene flow
Gene flow can occur when an individual travels from one geographic location to another.
Maintained gene flow between two populations can also lead to a combination of the two gene pools, reducing the genetic variation between the two groups. Gene flow strongly acts against speciation, by recombining the gene pools of the groups, and thus, repairing the developing differences in genetic variation that would have led to full speciation and creation of daughter species.
For example, if a species of grass grows on both sides of a highway, pollen is likely to be transported from one side to the other and vice versa. If this pollen is able to fertilize the plant where it ends up and produce viable offspring, then the alleles in the pollen have effectively linked the population on one side of the highway with the other.
Mutation
Mutations are changes to an organism's DNA and are an important driver of diversity in populations. Species evolve because of the accumulation of mutations that occur over time. The appearance of new mutations is the most common way to introduce novel genotypic and phenotypic variance. Some mutations are unfavorable or harmful and are quickly eliminated from the population by natural selection. Others are beneficial and will spread through the population. Whether or not a mutation is beneficial or harmful is determined by whether it helps an organism survive to sexual maturity and reproduce. Some mutations have no effect on an organism and can linger, unaffected by natural selection, in the genome while others can have a dramatic effect on a gene and the resulting phenotype.
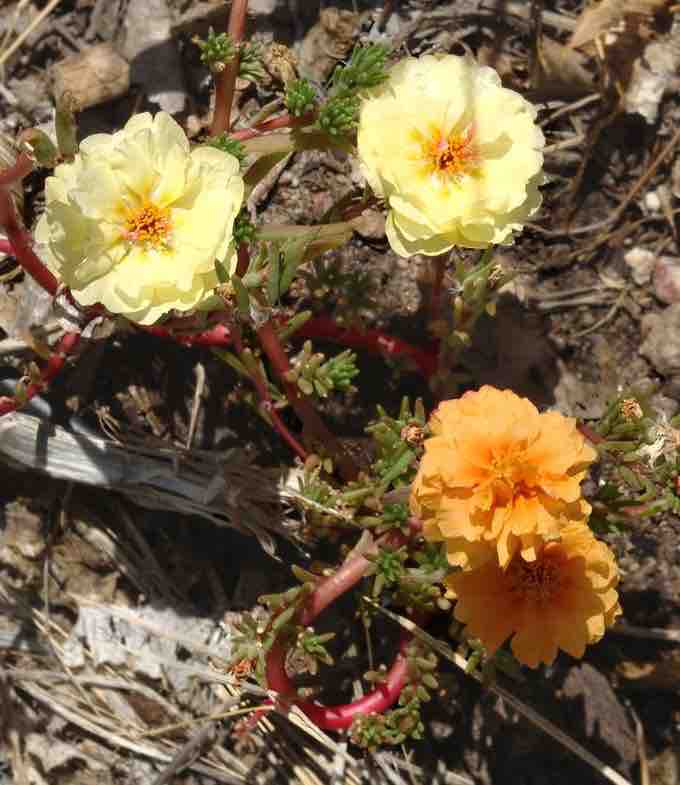

Mutation in a garden rose
A mutation has caused this garden moss rose to produce flowers of different colors. This mutation has introduce a new allele into the population that increases genetic variation and may be passed on to the next generation.