Meiosis II
Meiosis II initiates immediately after cytokinesis, usually before the chromosomes have fully decondensed. In contrast to meiosis I, meiosis II resembles a normal mitosis. In some species, cells enter a brief interphase, or interkinesis, before entering meiosis II. Interkinesis lacks an S phase, so chromosomes are not duplicated. The two cells produced in meiosis I go through the events of meiosis II together. During meiosis II, the sister chromatids within the two daughter cells separate, forming four new haploid gametes. The mechanics of meiosis II is similar to mitosis, except that each dividing cell has only one set of homologous chromosomes.
Prophase II
If the chromosomes decondensed in telophase I, they condense again. If nuclear envelopes were formed, they fragment into vesicles. The centrosomes that were duplicated during interphase I move away from each other toward opposite poles and new spindles are formed.
Prometaphase II
The nuclear envelopes are completely broken down and the spindle is fully formed. Each sister chromatid forms an individual kinetochore that attaches to microtubules from opposite poles.
Metaphase II
The sister chromatids are maximally condensed and aligned at the equator of the cell.
Anaphase II
The sister chromatids are pulled apart by the kinetochore microtubules and move toward opposite poles. Non-kinetochore microtubules elongate the cell .
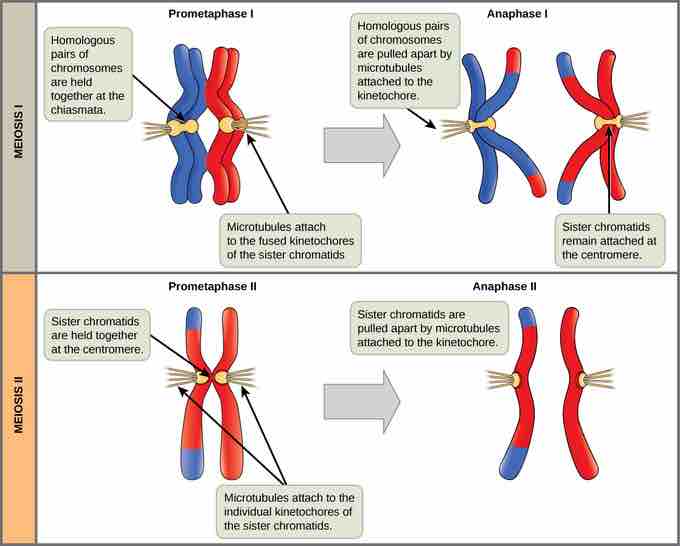
Meiosis I vs. Meiosis II
The process of chromosome alignment differs between meiosis I and meiosis II. In prometaphase I, microtubules attach to the fused kinetochores of homologous chromosomes, and the homologous chromosomes are arranged at the midpoint of the cell in metaphase I. In anaphase I, the homologous chromosomes are separated. In prometaphase II, microtubules attach to the kinetochores of sister chromatids, and the sister chromatids are arranged at the midpoint of the cells in metaphase II. In anaphase II, the sister chromatids are separated.
Telophase II and Cytokinesis
The chromosomes arrive at opposite poles and begin to decondense. Nuclear envelopes form around the chromosomes. Cytokinesis separates the two cells into four unique haploid cells. At this point, the newly-formed nuclei are both haploid. The cells produced are genetically unique because of the random assortment of paternal and maternal homologs and because of the recombining of maternal and paternal segments of chromosomes (with their sets of genes) that occurs during crossover .
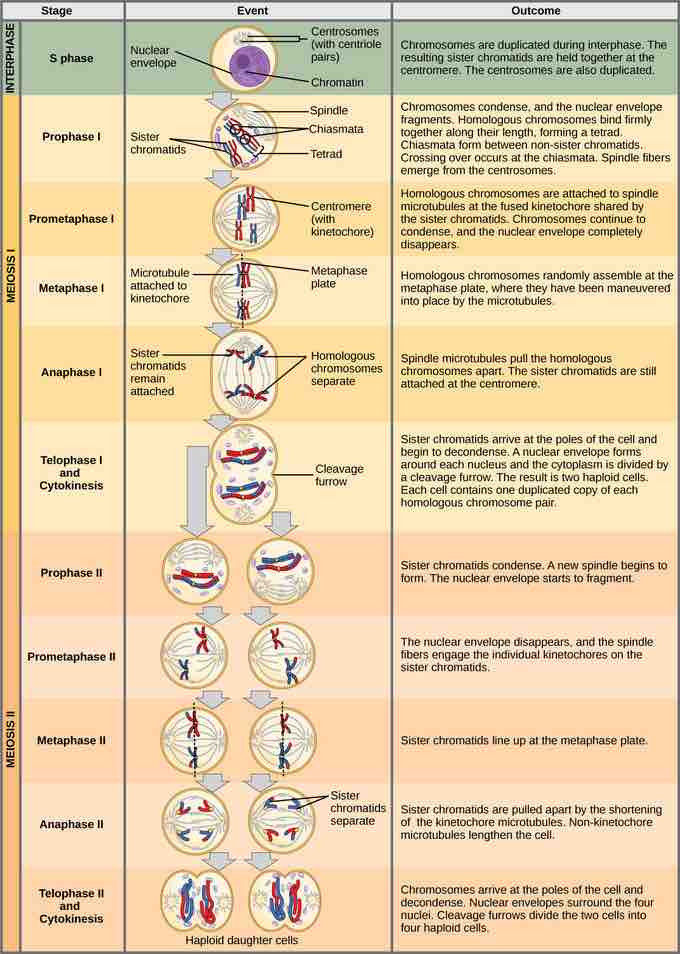
Complete Stages of Meiosis
An animal cell with a diploid number of four (2n = 4) proceeds through the stages of meiosis to form four haploid daughter cells.