Section 3
Superphylum Lophotrochozoa
By Boundless

The Lophotrochozoa are protostomes possessing a blastopore, an early form of a mouth; they include the trochozoans and the lophophorata.
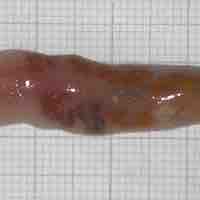
The Platyhelminthes are flatworms that lack a coelom; many are parasitic; all lack either a circulatory or respiratory system.
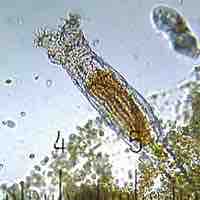
Rotifers are microscopic organisms named for a rotating structure (called the corona) at their anterior end that is covered with cilia.
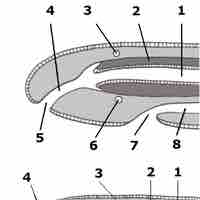
Nemertea, or ribbon worms, are distinguished by their proboscis, used for capturing prey and enclosed in a cavity called a rhynchocoel.

Mollusks have a soft body and share several characteristics, including a muscular foot, a visceral mass of internal organs, and a mantle.
The phylum Mollusca includes a wide variety of animals including the gastropods ("stomach foot"), the cephalopods ("head foot"), and the scaphopods ("boat foot").
Annelids include segmented worms, such as leeches and earthworms; they are the most advanced worms as they possess a true coelom.