Fundamental Concepts in Accounting
Financial statements are prepared according to agreed upon guidelines. In order to understand these guidelines, it helps to understand the objectives of financial reporting. The objectives of financial reporting, as discussed in the Financial Accounting standards Board (FASB) Statement of Financial Accounting Concepts No. 1, are to provide information that
- Is useful to existing and potential investors and creditors and other users in making rational investment, credit, and similar decisions;
- Helps existing and potential investors and creditors and other users to assess the amounts, timing, and uncertainty of prospective net cash inflows to the enterprise;
- Identifies the economic resources of an enterprise, the claims to those resources, and the effects that transactions, events, and circumstances have on those resources.
Preparing Financial Statements
In order to prepare the financial statements, it is important to adhere to certain fundamental accounting concepts.
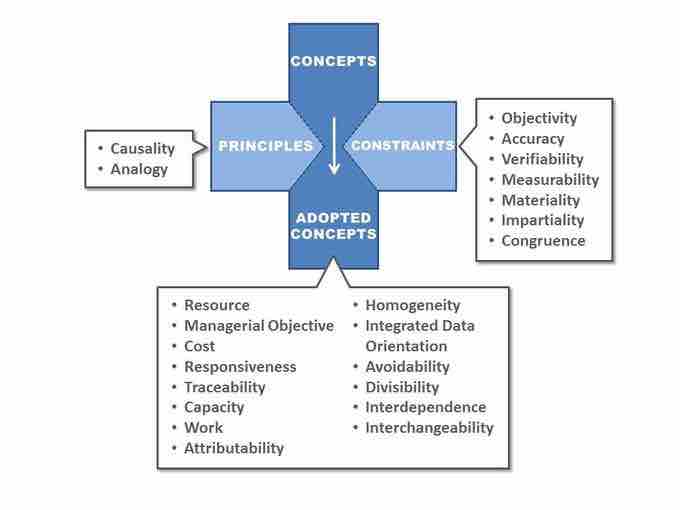
Accounting Concepts in a Diagram
This is a diagram of details for principles, concepts, and constraints within the field of Financial Accounting.
- Going Concern, unless there is evidence to the contrary, it is assumed that a business will continue to trade normally for the foreseeable future.
- Accruals and Matching, revenue earned must be matched against expenditure when it was incurred
- Prudence, if there are two acceptable accounting procedures choose the one gives the less optimistic view of profitability and asset values.
- Consistency, similar items should be accorded similar accounting treatments.
- Entity, a business is an entity distinct from its owners.
- Money Measurement, accounts only deal with items to which monetary values can be attributed.
- Separate Valuation each asset or liability must be valued separately.
- Materiality, only items material in amount or in their nature will affect the true and fair view given by a set of accounts.
- Historical Cost, tTransactions are recorded at the cost when they occurred.
- Realization, revenue and profits are recognized when realized.
- Duality, every transaction has two effects.