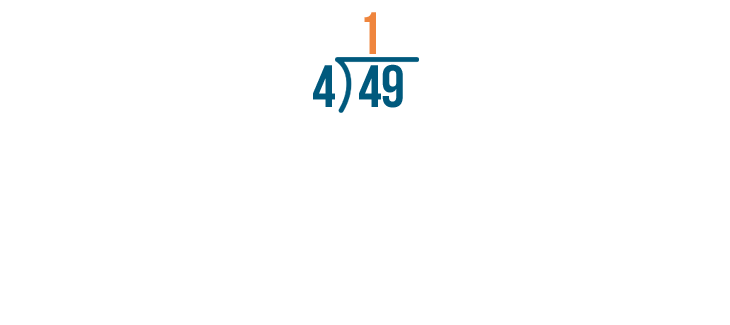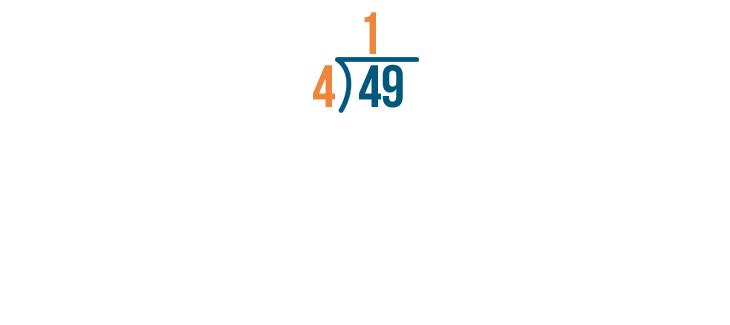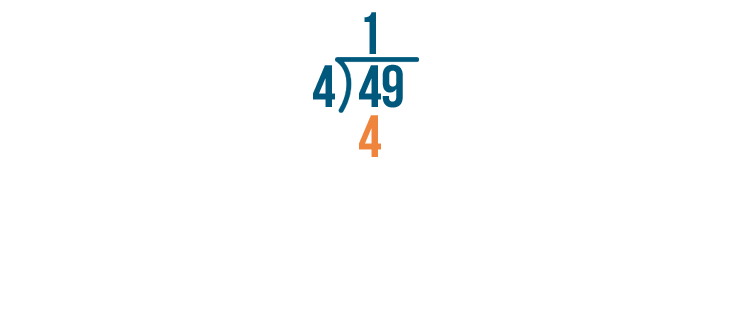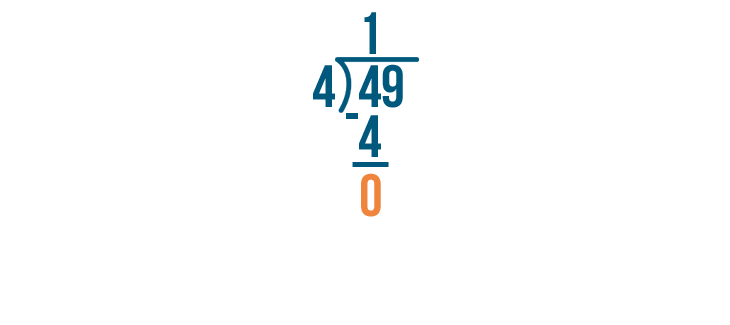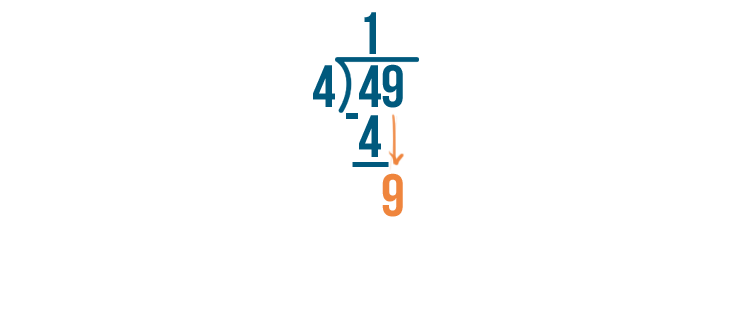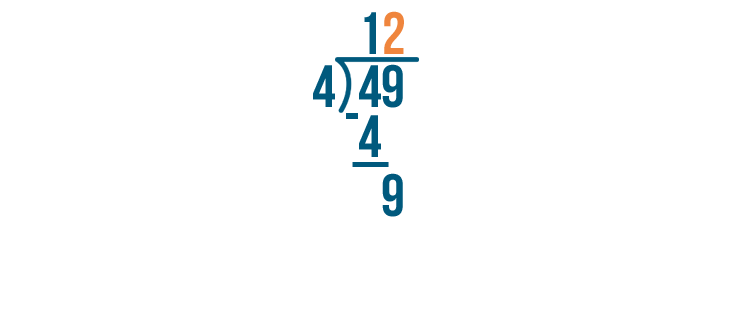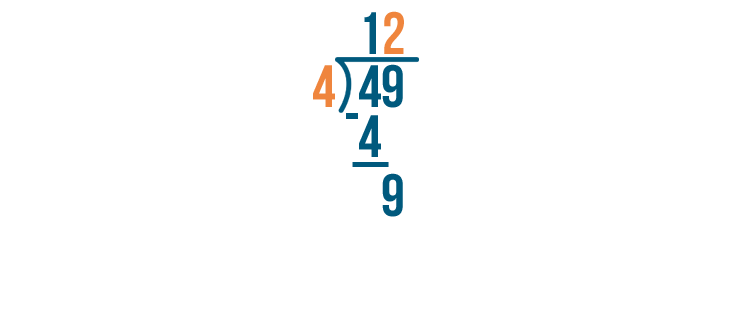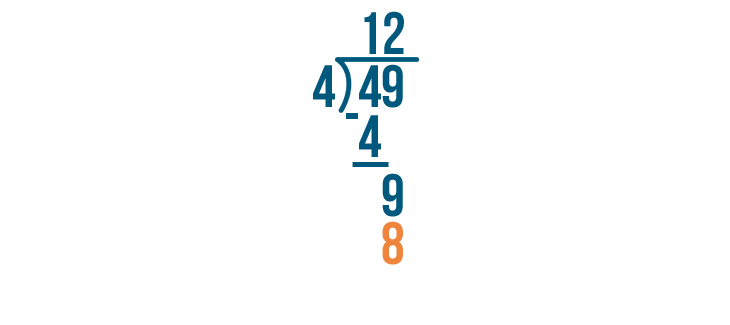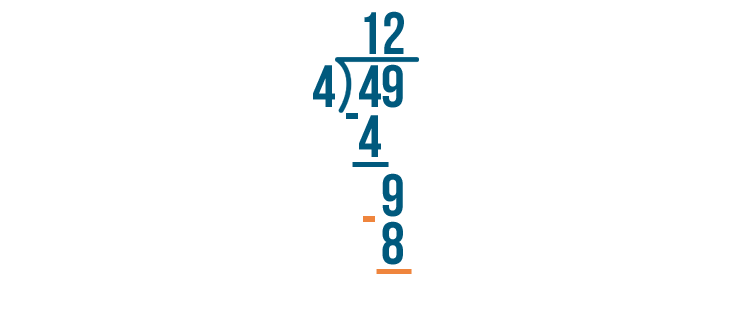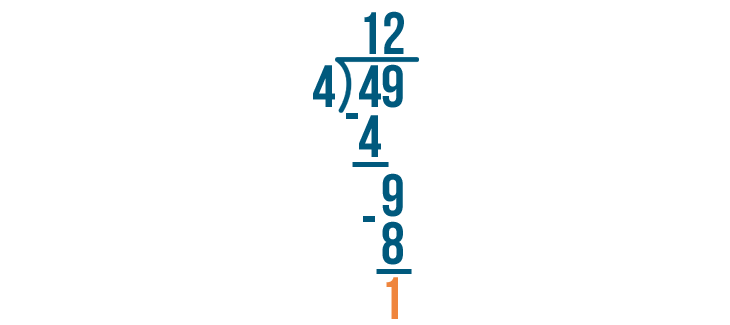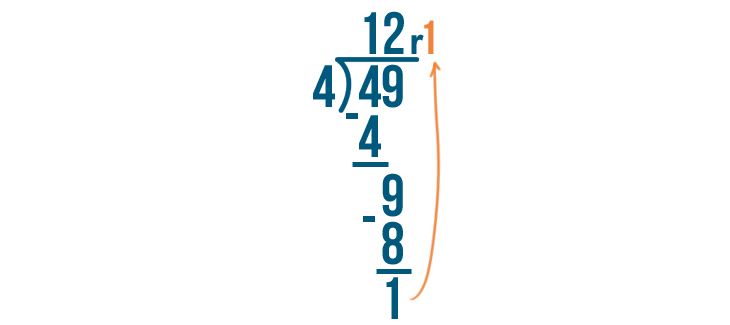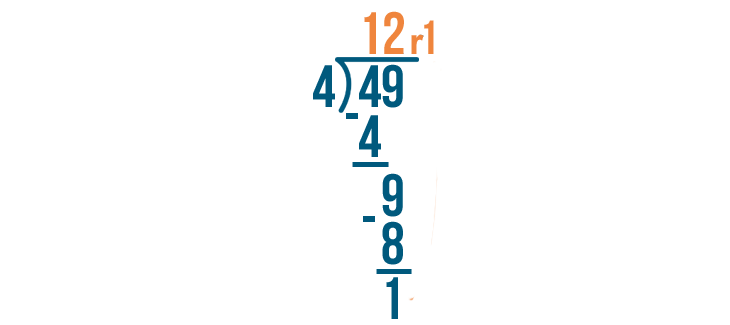Problems with Remainders
In Lesson 3, you learned that some numbers can't be equally divided. When that happens, there will be an amount left over. This is called a remainder. For instance, let's say you want to share 8 treats equally among your 3 dogs. The answer is that each dog would get two treats with a remainder of two.
The remainder is written as part of the quotient: 8 / 3 = 2 r2.
Long division problems can have remainders too. Watch the slideshow to see how.

Let's try this problem, 49 / 4.

As always, start by dividing the left digit. This means we'll solve for 4 / 4.
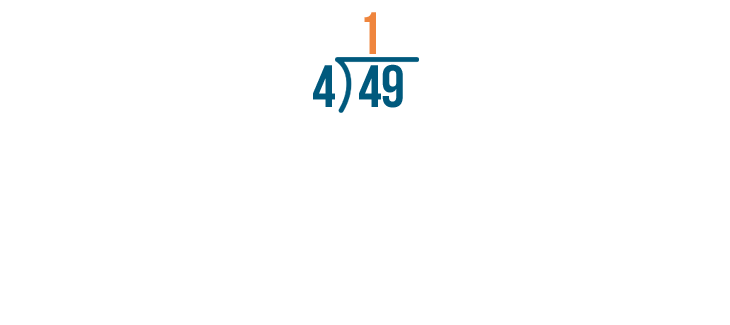
4 / 4 is 1.
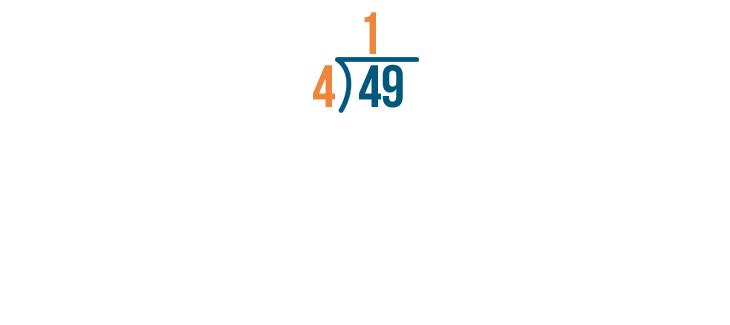
Next, we'll multiply the answer we just got, 1, by the number we're dividing by, 4. So 4 x 1.
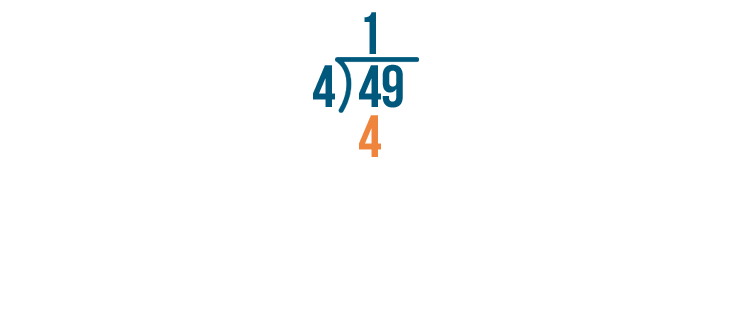
4 x 1 is 4.
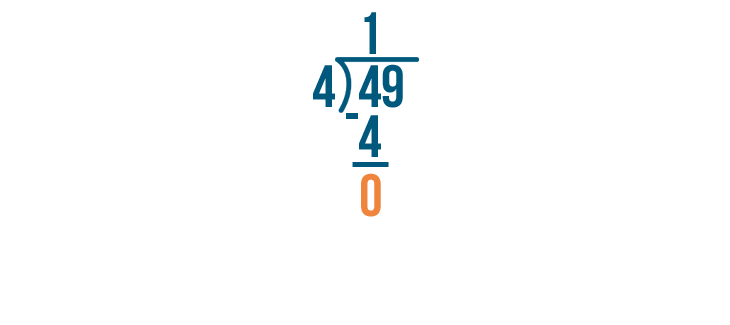
Next, subtract 4 - 4. Whenever you subtract a number from the same number, the answer is 0. So 4 - 4 = 0.
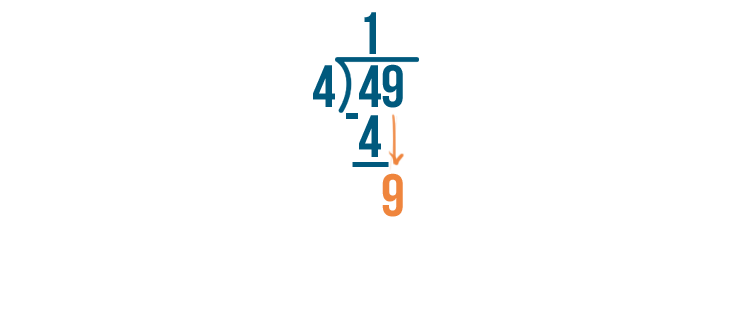
Our problem's not done. The next digit in the number we're dividing is 9. We'll solve for 9 / 4.
-
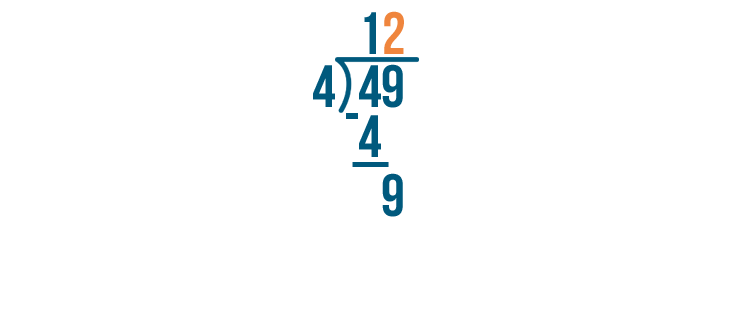
9 / 4 is 2.
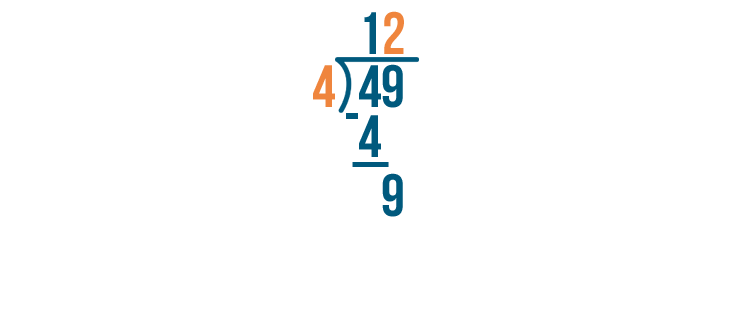
Again, we'll multiply the number we just wrote by the number we're dividing by.
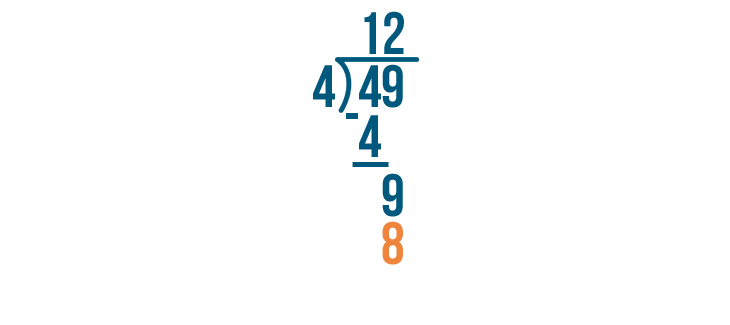
2 x 4 is 8.
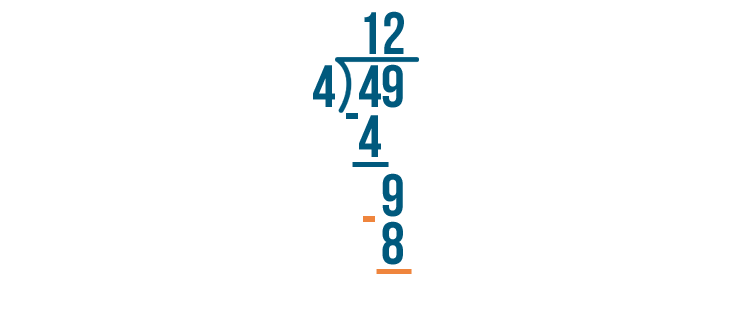
We'll subtract that number, 8, from the number we were dividing.
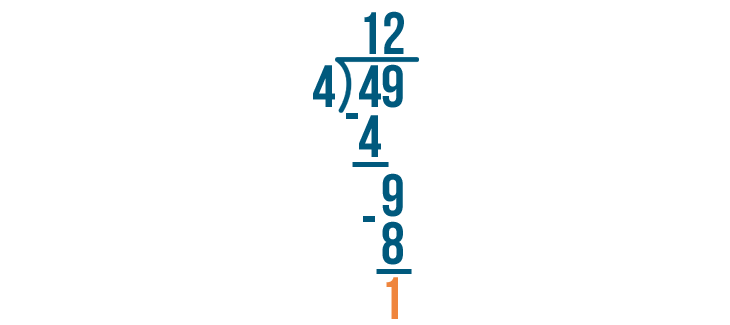
9 - 8 is 1.
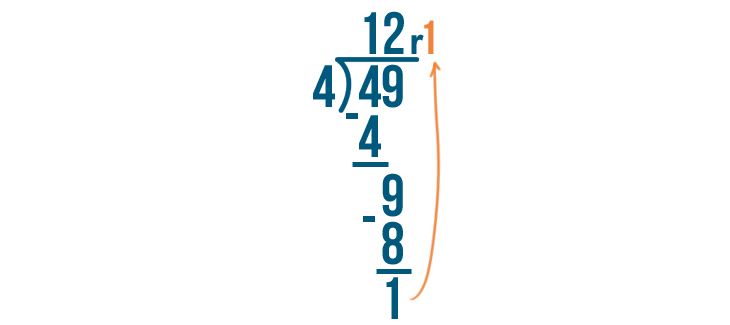
Since 1 is smaller than 4, we can't divide it any further. 1 is our remainder. We'll write it next to the rest of the answer.
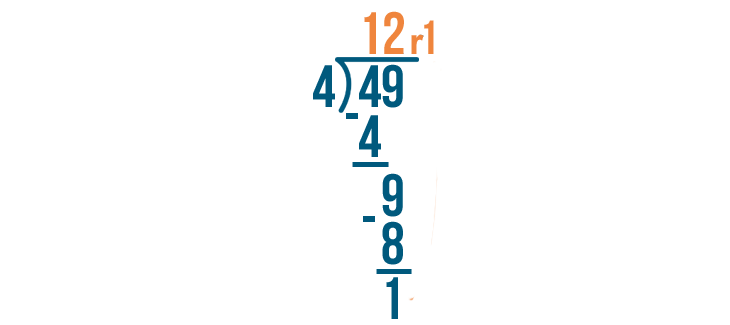
We're done! 49 / 4 = 12, with a remainder of 1.
-
Now click these and try it.. Solve these division problems with remainders.
Problem 1
Problem 2
Problem 3